Multi-detector row CT angiography with direct intra-arterial contrast injection for the evaluation of neurovascular disease: technique, applications, and initial experience
- PMID: 19213819
- PMCID: PMC7051659
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1438
Multi-detector row CT angiography with direct intra-arterial contrast injection for the evaluation of neurovascular disease: technique, applications, and initial experience
Abstract
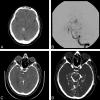
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of 64-section multi-detector row CT angiography (CTA) with direct intra-arterial contrast injection (IA-CTA) for the evaluation of neurovascular disease. This technique was used in 11 patients at our institution. All studies were technically successful, and there were no complications. Small vascular malformations were mapped easily on high-resolution IA-CTA images, enabling microsurgical resection or stereotactic radiosurgery. In a similar fashion, additional morphologic features were revealed on IA-CTA images not seen on standard 2D and 3D digital subtraction angiography. Of 11 patients undergoing IA-CTA, 7 patients had further anatomic clarity of the small arteriovenous fistula/malformation and 4 patients had changes in the treatment plan on the basis of the IA-CTA findings.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Initial experience with a combined multidetector CT and biplane digital subtraction angiography suite with a single interactive table for the diagnosis and treatment of neurovascular disease.J Neurointerv Surg. 2013 Jan 1;5(1):73-80. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2011-010092. Epub 2011 Sep 27. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013. PMID: 21990532
-
Detection of intracranial aneurysms using three-dimensional multidetector-row CT angiography: is bone subtraction necessary?Eur J Radiol. 2011 Aug;79(2):e18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Eur J Radiol. 2011. PMID: 20144517
-
In vivo X-ray digital subtraction and CT angiography of the murine cerebrovasculature using an intra-arterial route of contrast injection.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012 Oct;33(9):1702-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3071. Epub 2012 May 10. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012. PMID: 22576899 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic imaging of cerebrovascular disease on multi-detector row computed tomography (MDCT)].Brain Nerve. 2011 Sep;63(9):923-32. Brain Nerve. 2011. PMID: 21878694 Review. Japanese.
-
Image-guided microneurosurgical management of vascular lesions using navigated computed tomography angiography. An advanced IGS technology application.Int J Med Robot. 2006 Jun;2(2):161-7. doi: 10.1002/rcs.89. Int J Med Robot. 2006. PMID: 17520627 Review.
Cited by
-
Unintended intra-arterial injection of contrast of an intracranial CT angiography.Radiol Case Rep. 2018 Oct 6;14(1):41-43. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.09.005. eCollection 2019 Jan. Radiol Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30305864 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglossal canal dural arteriovenous fistula embolized under precise anatomical evaluation by selective intra-arterial injection computed tomography angiography.Interv Neuroradiol. 2015 Feb;21(1):88-93. doi: 10.15274/inr-2014-10104. Interv Neuroradiol. 2015. PMID: 25934781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vieco PT. CT angiography of the carotid artery. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 1998;8:593–605 - PubMed
-
- Gandhi D. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography in cervicocranial vascular disease. J Neuroophthalmol 2004;24:306–14 - PubMed
-
- van Gelder JM. Computed tomographic angiography for detecting cerebral aneurysms: implications of aneurysm size distribution for the sensitivity, specificity, and likelihood ratios. Neurosurgery 2003;53:597–605; discussion 605–06 - PubMed
-
- Kangasniemi M, Mäkelä T, Koskinen S, et al. Detection of intracranial aneurysms with two-dimensional and three-dimensional multislice helical computed tomographic angiography. Neurosurgery 2004;54:336–40; discussion 340–41 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
