Critical loss of the balance between Th17 and T regulatory cell populations in pathogenic SIV infection
- PMID: 19214220
- PMCID: PMC2635016
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000295
Critical loss of the balance between Th17 and T regulatory cell populations in pathogenic SIV infection
Abstract
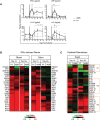
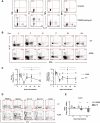
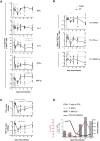
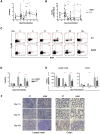
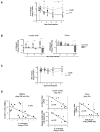
Chronic immune activation and progression to AIDS are observed after SIV infection in macaques but not in natural host primate species. To better understand this dichotomy, we compared acute pathogenic SIV infection in pigtailed macaques (PTs) to non-pathogenic infection in African green monkeys (AGMs). SIVagm-infected PTs, but not SIVagm-infected AGMs, rapidly developed systemic immune activation, marked and selective depletion of IL-17-secreting (Th17) cells, and loss of the balance between Th17 and T regulatory (Treg) cells in blood, lymphoid organs, and mucosal tissue. The loss of Th17 cells was found to be predictive of systemic and sustained T cell activation. Collectively, these data indicate that loss of the Th17 to Treg balance is related to SIV disease progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Hazenberg MD, Hamann D, Schuitemaker H, Miedema F. T cell depletion in HIV-1 infection: how CD4+ T cells go out of stock. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:285–289. - PubMed
-
- McCune JM. The dynamics of CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV disease. Nature. 2001;410:974–979. - PubMed
-
- Grossman Z, Meier-Schellersheim M, Sousa AE, Victorino RM, Paul WE. CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV infection: are we closer to understanding the cause? Nat Med. 2002;8:319–323. - PubMed
-
- Douek DC, Picker LJ, Koup RA. T cell dynamics in HIV-1 infection. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:265–304. - PubMed
-
- Heeney JL, Dalgleish AG, Weiss RA. Origins of HIV and the evolution of resistance to AIDS. Science. 2006;313:462–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI44480/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51RR000166/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI066917/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI076014/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007762/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 RR016354/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI030018/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI066917/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000169/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U51RR00169/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK060617/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24RR016354/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DPI OD00329/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI066314/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000166/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DA015625/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD000329/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30DA015625/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI076014/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

