Human cervical carcinoma xenograft models for studies of the physiological microenvironment of tumors
- PMID: 19214568
- PMCID: PMC12160152
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0558-8
Human cervical carcinoma xenograft models for studies of the physiological microenvironment of tumors
Abstract
Objective: To establish and characterize experimental tumor models of advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix.
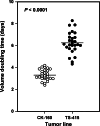
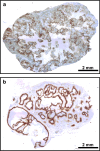
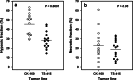
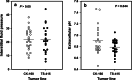
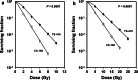
Methods: Permanent cell lines (CK-160 and TS-415) were established from pelvic lymph node metastases of two cervical carcinoma patients. Xenografted tumors were initiated by inoculating 5 x 10(5) cells into the gastrocnemius muscle of BALB/c nu/nu mice. The tumors were characterized with respect to histological appearance, fraction of necrotic tissue (NF), pimonidazole hypoxic fraction (HF(Pim)), interstitial fluid pressure (IFP), extracellular pH (pH(e)), metastatic propensity, and radiation sensitivity.
Results: The xenografted tumors reflected the donor patients' tumors in histological appearance, metastatic propensity, and radiation sensitivity and showed significant intertumor heterogeneity in growth rate, NF, HF(Pim), IFP, and pH(e).
Conclusions: CK-160 and TS-415 xenografts possess properties making them relevant models for studies of the physiological microenvironment of cervical carcinoma and its influence on metastatic dissemination and response to treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Averette HE, Nguyen HN, Donato DM et al (1993) Radical hysterectomy for invasive cervical cancer: a 25-year prospective experience with the Miami technique. Cancer 71:1422–1437 - PubMed
-
- Fyles A, Milosevic M, Wong R et al (1998) Oxygenation predicts radiation response and survival in patients with cervix cancer. Radiother Oncol 48:149–156. doi:10.1016/S0167-8140(98)00044-9 - PubMed
-
- Fyles A, Milosevic M, Pintilie M et al (2006) Long-term performance of interstitial fluid pressure and hypoxia as prognostic factors in cervix cancer. Radiother Oncol 80:132–137. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2006.07.014 - PubMed
-
- Gulliksrud K, Brurberg K, Rofstad EK (2008) Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of tumor interstitial fluid pressure. Radiother Oncol [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2008.08.015 - PubMed
-
- Hall EJ, Giaccia AJ (2006) Radiobiology for the radiologist, chapter 6. Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

