Biomathematical modeling of pulsatile hormone secretion: a historical perspective
- PMID: 19216934
- PMCID: PMC2662597
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)03814-7
Biomathematical modeling of pulsatile hormone secretion: a historical perspective
Abstract
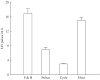
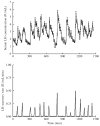
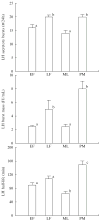
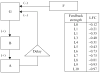
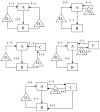
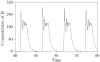
Shortly after the recognition of the profound physiological significance of the pulsatile nature of hormone secretion, computer-based modeling techniques were introduced for the identification and characterization of such pulses. Whereas these earlier approaches defined perturbations in hormone concentration-time series, deconvolution procedures were subsequently employed to separate such pulses into their secretion event and clearance components. Stochastic differential equation modeling was also used to define basal and pulsatile hormone secretion. To assess the regulation of individual components within a hormone network, a method that quantitated approximate entropy within hormone concentration-times series was described. To define relationships within coupled hormone systems, methods including cross-correlation and cross-approximate entropy were utilized. To address some of the inherent limitations of these methods, modeling techniques with which to appraise the strength of feedback signaling between and among hormone-secreting components of a network have been developed. Techniques such as dynamic modeling have been utilized to reconstruct dose-response interactions between hormones within coupled systems. A logical extension of these advances will require the development of mathematical methods with which to approximate endocrine networks exhibiting multiple feedback interactions and subsequently reconstruct their parameters based on experimental data for the purpose of testing regulatory hypotheses and estimating alterations in hormone release control mechanisms.
Figures



References
-
- Atkinson LE, Bhattacharya AN, Monroe SE, Dierschke DJ, Knobil E. Effects of gonadectomy on plasma LH concentration in the rhesus monkey. Endocrinology. 1970;87:847–849. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom CT, McNeilly AS, Leask RM, Baird DT. Pulsatile secretion of LH, FSH, prolactin, oestradiol and progesterone during the human menstrual cycle. Clin Endocrinol. 1982;17:29–42. - PubMed
-
- Bergman RN, Ider YZ, Bowden CR, Cobelli C. Quantitative estimation of insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol. 1979;236:E667–E677. - PubMed
-
- Booth RA, Jr, Weltman JY, Yankov VI, Murray J, Davison TS, Rogol AD, Asplin CM, Johnson ML, Veldhuis JD, Evans WS. Mode of pulsatile follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in gonadal hormone-sufficient and -deficient women: A clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:3208–3214. - PubMed
-
- Burger CW, Korsen T, van Kessel H, van Dop PA, Caron FJ, Schoemaker J. Pulsatile luteinizing hormone patterns in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle, polycystic ovarian disease (PCOD) and non-PCOD secondary amenorrhea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985;61:1126–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

