The sumLINK statistic for genetic linkage analysis in the presence of heterogeneity
- PMID: 19217022
- PMCID: PMC3409837
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.20414
The sumLINK statistic for genetic linkage analysis in the presence of heterogeneity
Abstract
We present the "sumLINK" statistic--the sum of multipoint LOD scores for the subset of pedigrees with nominally significant linkage evidence at a given locus--as an alternative to common methods to identify susceptibility loci in the presence of heterogeneity. We also suggest the "sumLOD" statistic (the sum of positive multipoint LOD scores) as a companion to the sumLINK. sumLINK analysis identifies genetic regions of extreme consistency across pedigrees without regard to negative evidence from unlinked or uninformative pedigrees. Significance is determined by an innovative permutation procedure based on genome shuffling that randomizes linkage information across pedigrees. This procedure for generating the empirical null distribution may be useful for other linkage-based statistics as well. Using 500 genome-wide analyses of simulated null data, we show that the genome shuffling procedure results in the correct type 1 error rates for both the sumLINK and sumLOD. The power of the statistics was tested using 100 sets of simulated genome-wide data from the alternative hypothesis from GAW13. Finally, we illustrate the statistics in an analysis of 190 aggressive prostate cancer pedigrees from the International Consortium for Prostate Cancer Genetics, where we identified a new susceptibility locus. We propose that the sumLINK and sumLOD are ideal for collaborative projects and meta-analyses, as they do not require any sharing of identifiable data between contributing institutions. Further, loci identified with the sumLINK have good potential for gene localization via statistical recombinant mapping, as, by definition, several linked pedigrees contribute to each peak.
Figures

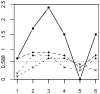

References
-
- Abecasis G, Cherny S, Cookson W, Cardon L. Merlin-rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet. 2002;30:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Camp NJ, Farnham JM, Allen-Brady K, Cannon-Albright LA. Statistical recombinant mapping in extended high-risk Utah pedigrees narrows the 8q24 prostate cancer locus to 2.0 Mb. Prostate. 2007;67(13):1456–64. - PubMed
-
- Camp NJ, Farnham JM, Cannon-Albright LA. Localization of a prostate cancer predisposition gene to an 880-kb region on chromosome 22q12.3 in Utah high-risk pedigrees. Cancer Research. 2006;66(20):10205–12. - PubMed
-
- Camp NJ, Hopkins PN, Hasstedt SJ, Coon H, Malhotra A, Cawthon RM, Hunt SC. Genome-Wide Multipoint Parametric Linkage Analysis of Pulse Pressure in Large, Extended Utah Pedigrees. Hypertension. 2003;43:322–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

