Fission yeast Scm3: A CENP-A receptor required for integrity of subkinetochore chromatin
- PMID: 19217404
- PMCID: PMC2697330
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.019
Fission yeast Scm3: A CENP-A receptor required for integrity of subkinetochore chromatin
Abstract
The mechanisms ensuring specific incorporation of CENP-A at centromeres are poorly understood. Mis16 and Mis18 are required for CENP-A localization at centromeres and form a complex that is conserved from fission yeast to human. Fission yeast sim1 mutants that alleviate kinetochore domain silencing are defective in Scm3(Sp), the ortholog of budding yeast Scm3(Sc). Scm3(Sp) depends on Mis16/18 for its centromere localization and like them is recruited to centromeres in late anaphase. Importantly, Scm3(Sp) coaffinity purifies with CENP-A(Cnp1) and associates with CENP-A(Cnp1) in vitro, yet localizes independently of intact CENP-A(Cnp1) chromatin and is differentially released from chromatin. While Scm3(Sc) has been proposed to form a unique hexameric nucleosome with CENP-A(Cse4) and histone H4 at budding yeast point centromeres, we favor a model in which Scm3(Sp) acts as a CENP-A(Cnp1) receptor/assembly factor, cooperating with Mis16 and Mis18 to receive CENP-A(Cnp1) from the Sim3 escort and mediate assembly of CENP-A(Cnp1) into subkinetochore chromatin.
Figures
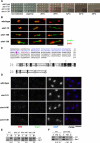

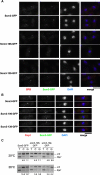

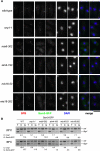
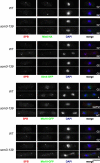
Comment in
-
CENP-A targeting moves a step back.Mol Cell. 2009 Feb 27;33(4):411-3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.02.006. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19250900
References
-
- Allshire R.C., Javerzat J.P., Redhead N.J., Cranston G. Position effect variegation at fission yeast centromeres. Cell. 1994;76:157–169. - PubMed
-
- Allshire R.C., Nimmo E.R., Ekwall K., Javerzat J.P., Cranston G. Mutations derepressing silent centromeric domains in fission yeast disrupt chromosome segregation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:218–233. - PubMed
-
- Bhargava M.M., Cramer J.H., Halvorson H.O. Isolation of high molecular weight DNA from yeast nuclei. Anal. Biochem. 1972;49:276–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

