Cardiac fibroblasts regulate myocardial proliferation through beta1 integrin signaling
- PMID: 19217425
- PMCID: PMC2664087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.12.007
Cardiac fibroblasts regulate myocardial proliferation through beta1 integrin signaling
Abstract
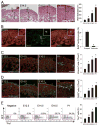
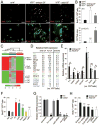
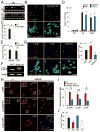
Growth and expansion of ventricular chambers is essential during heart development and is achieved by proliferation of cardiac progenitors. Adult cardiomyocytes, by contrast, achieve growth through hypertrophy rather than hyperplasia. Although epicardial-derived signals may contribute to the proliferative process in myocytes, the factors and cell types responsible for development of the ventricular myocardial thickness are unclear. Using a coculture system, we found that embryonic cardiac fibroblasts induced proliferation of cardiomyocytes, in contrast to adult cardiac fibroblasts that promoted myocyte hypertrophy. We identified fibronectin, collagen, and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor as embryonic cardiac fibroblast-specific signals that collaboratively promoted cardiomyocyte proliferation in a paracrine fashion. Myocardial beta1-integrin was required for this proliferative response, and ventricular cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of beta1-integrin in mice resulted in reduced myocardial proliferation and impaired ventricular compaction. These findings reveal a previously unrecognized paracrine function of embryonic cardiac fibroblasts in regulating cardiomyocyte proliferation.
Figures



Comment in
-
Fibroblasts inform the heart: control of cardiomyocyte cycling and size by age-dependent paracrine signals.Dev Cell. 2009 Feb;16(2):161-2. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.01.020. Dev Cell. 2009. PMID: 19217417 Review.
References
-
- Baudino TA, Carver W, Giles W, Borg TK. Cardiac fibroblasts: friend or foe? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;291:H1015–1026. - PubMed
-
- Camelliti P, Borg TK, Kohl P. Structural and functional characterisation of cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65:40–51. - PubMed
-
- Demayo F, Minoo P, Plopper CG, Schuger L, Shannon J, Torday JS. Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions in lung development and repair: are modeling and remodeling the same process? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002;283:L510–517. - PubMed
-
- Dettman RW, Denetclaw W, Jr, Ordahl CP, Bristow J. Common epicardial origin of coronary vascular smooth muscle, perivascular fibroblasts, and intermyocardial fibroblasts in the avian heart. Dev Biol. 1998;193:169–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

