Inactivation of murine Usp1 results in genomic instability and a Fanconi anemia phenotype
- PMID: 19217432
- PMCID: PMC3134285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.01.001
Inactivation of murine Usp1 results in genomic instability and a Fanconi anemia phenotype
Abstract
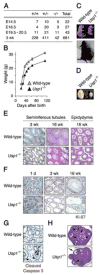
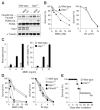
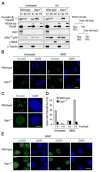
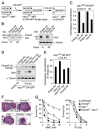
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a human genetic disease characterized by chromosome instability, cancer predisposition, and cellular hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents. The FA pathway regulates the repair of DNA crosslinks. A critical step in this pathway is the monoubiquitination and deubiquitination of FANCD2. Deubiquitination of FANCD2 is mediated by the ubiquitin protease, USP1. Here, we demonstrate that targeted deletion of mouse Usp1 results in elevated perinatal lethality, male infertility, crosslinker hypersensitivity, and an FA phenotype. Usp1(-/-) mouse embryonic fibroblasts had heightened levels of monoubiquitinated Fancd2 in chromatin. Usp1(-/-) cells exhibited impaired Fancd2 foci assembly and a defect in homologous recombination repair. Double knockout of Usp1 and Fancd2 resulted in a more severe phenotype than either single knockout. Our results indicate that mouse Usp1 functions downstream in the FA pathway. Deubiquitination is a critical event required for Fancd2 nuclear foci assembly, release from chromatin, and function in DNA repair.
Figures
References
-
- Agoulnik AI, Lu B, Zhu Q, Truong C, Ty MT, Arango N, Chada KK, Bishop CE. A novel gene, Pog, is necessary for primordial germ cell proliferation in the mouse and underlies the germ cell deficient mutation, gcd. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:3047–3053. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Tomkins DJ, Auerbach W, McKerlie C, Youssoufian H, Liu L, Gan O, Carreau M, Auerbach A, Groves T, et al. Inactivation of Fac in mice produces inducible chromosomal instability and reduced fertility reminiscent of Fanconi anaemia. Nature Genetics. 1996;12:448–451. - PubMed
-
- Cheung AM, Elia A, Tsao MS, Done S, Wagner KU, Hennighausen L, Hakem R, Mak TW. Brca2 deficiency does not impair mammary epithelium development but promotes mammary adenocarcinoma formation in p53+/− mutant mice. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1959–1965. - PubMed
-
- Cohn MA, Kowal P, Yang K, Haas W, Huang TT, Gygi SP, D'Andrea AD. A UAF1-containing multisubunit protein complex regulates the Fanconi anemia pathway. Mol Cell. 2007;28:786–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

