Effects of multiple occupancy and interparticle interactions on selective transport through narrow channels: theory versus experiment
- PMID: 19217844
- PMCID: PMC2717243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.09.058
Effects of multiple occupancy and interparticle interactions on selective transport through narrow channels: theory versus experiment
Abstract
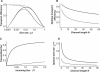
Many biological and artificial transport channels function without direct input of metabolic energy during a transport event and without structural rearrangements involving transitions from a closed to an open state. Nevertheless, such channels are able to maintain efficient and selective transport. It has been proposed that attractive interactions between the transported molecules and the channel can increase the transport efficiency and that the selectivity of such channels can be based on the strength of the interaction of the specifically transported molecules with the channel. Herein, we study the transport through narrow channels in a framework of a general kinetic theory, which naturally incorporates multiparticle occupancy of the channel and non-single-file transport. We study how the transport efficiency and the probability of translocation through the channel are affected by interparticle interactions in the confined space inside the channel, and establish conditions for selective transport. We compare the predictions of the model with the available experimental data and find good semiquantitative agreement. Finally, we discuss applications of the theory to the design of artificial nanomolecular sieves.
Figures



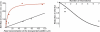

Similar articles
-
Effects of jamming on nonequilibrium transport times in nanochannels.Phys Rev Lett. 2009 Sep 18;103(12):128103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.128103. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Phys Rev Lett. 2009. PMID: 19792464 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of transport selectivity through nano-channels by non-specific competition.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Jun 10;6(6):e1000804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000804. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 20548778 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the potential landscape on the single-file diffusion through channels.J Chem Phys. 2014 Dec 14;141(22):224901. doi: 10.1063/1.4903175. J Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 25494767
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
-
The properties of bio-energy transport and influence of structure nonuniformity and temperature of systems on energy transport along polypeptide chains.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012 Jan;108(1-2):1-46. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Sep 17. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21951575 Review.
Cited by
-
Physics of the Nuclear Pore Complex: Theory, Modeling and Experiment.Phys Rep. 2021 Jul 25;921:1-53. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2021.03.003. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Phys Rep. 2021. PMID: 35892075 Free PMC article.
-
Fluxes of non-interacting and strongly repelling particles through a single conical channel: Analytical results and their numerical tests.Chem Phys. 2010 Oct 5;375(2-3):523-528. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphys.2010.04.040. Chem Phys. 2010. PMID: 21057663 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role for transporter isoforms in optimizing membrane transport.Biophys J. 2011 Jul 20;101(2):L14-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.06.004. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21767474 Free PMC article.
-
Direct detection of molecular intermediates from first-passage times.Sci Adv. 2020 May 1;6(18):eaaz4642. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz4642. eCollection 2020 May. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32494675 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalization of a nanopore: the nuclear pore complex paradigm.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Oct;1793(10):1533-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.06.003. Epub 2009 Jul 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19596381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberts B., Bray D., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K. Garland Publishing; Boca Raton, FL: 1994. Molecular Biology of the Cell.
-
- Bezrukov S., Kullman L., Winterhalter M. Probing sugar translocation through maltoporin at the single channel level. FEBS Lett. 2000;476:224–228. - PubMed
-
- de Groot B.L., Grubmuller H. Water permeation across biological membranes: mechanism and dynamics of Aquaporin-1 and GlpF. Science. 2001;294:2353–2357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

