Interleukin-13-induced MUC5AC is regulated by 15-lipoxygenase 1 pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 19218191
- PMCID: PMC2675565
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200811-1744OC
Interleukin-13-induced MUC5AC is regulated by 15-lipoxygenase 1 pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
Rationale: 15-Lipoxygenase-1 (15LO1) and MUC5AC are highly expressed in asthmatic epithelial cells. IL-13 is known to induce 15LO1 and MUC5AC in human airway epithelial cells in vitro. Whether 15LO1 and/or its product 15-HETE modulate MUC5AC expression is unknown.
Objectives: To determine the expression of 15LO1 in freshly harvested epithelial cells from subjects with asthma and normal control subjects and to determine whether IL-13-induced 15LO1 expression and activation regulate MUC5AC expression in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro.
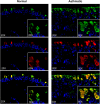
Methods: Human airway epithelial cells from subjects with asthma and normal subjects were evaluated ex vivo for 15LO1 and MUC5AC expression. The impact of 15LO1 on MUC5AC expression in vitro was analyzed by inhibiting 15LO1 through pharmacologic (PD146176) and siRNA approaches in human bronchial epithelial cells cultured under air-liquid interface. We analyzed 15 hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15-HETE) by liquid chromatography/UV/mass spectrometry. MUC5AC and 15LO1 were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR, immunofluoresence, and Western blot.
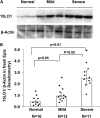
Measurements and main results: Epithelial 15LO1 expression increased with asthma severity (P < 0.0001). 15LO1 significantly correlated with MUC5AC ex vivo and in vitro. IL-13 increased 15LO1 expression and stimulated formation of two molecular species of 15-HETE esterified to phosphotidylethanolamine (15-HETE-PE). Inhibition of 15LO1 suppressed 15-HETE-PE and decreased MUC5AC expression in the presence of IL-13 stimulation. The addition of exogenous 15-HETE partially restored MUC5AC expression.
Conclusions: Epithelial 15LO1 expression increases with increasing asthma severity. IL-13 induction of 15-HETE-PE enhances MUC5AC expression in human airway epithelial cells. High levels of 15LO1 activity could contribute to the increases of MUC5AC observed in asthma.
Figures


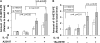




References
-
- Sullivan AF, Schatz M, Wenzel SE, Vanderweil SG, Camargo CA Jr. A profile of U.S. asthma centers, 2006. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2007;99:419–423. - PubMed
-
- Kondo M, Tamaoki J, Takeyama K, Nakata J, Nagai A. Interleukin-13 induces goblet cell differentiation in primary cell culture from guinea pig tracheal epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2002;27:536–541. - PubMed
-
- Kondo M, Tamaoki J, Takeyama K, Isono K, Kawatani K, Izumo T, Nagai A. Elimination of IL-13 reverses established goblet cell metaplasia into ciliated epithelia in airway epithelial cell culture. Allergol Int 2006;55:329–336. - PubMed
-
- Morcillo EJ, Cortijo J. Mucus and MUC in asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2006;12:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Fahy JV. Goblet cell and mucin gene abnormalities in asthma. Chest 2002;122:320S–326S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

