Efficient gene replacements in Toxoplasma gondii strains deficient for nonhomologous end joining
- PMID: 19218423
- PMCID: PMC2669201
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00357-08
Efficient gene replacements in Toxoplasma gondii strains deficient for nonhomologous end joining
Abstract
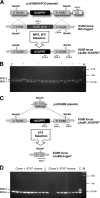
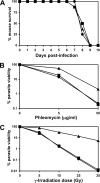
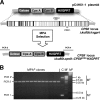
A high frequency of nonhomologous recombination has hampered gene targeting approaches in the model apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. To address whether the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) DNA repair pathway could be disrupted in this obligate intracellular parasite, putative KU proteins were identified and a predicted KU80 gene was deleted. The efficiency of gene targeting via double-crossover homologous recombination at several genetic loci was found to be greater than 97% of the total transformants in KU80 knockouts. Gene replacement efficiency was markedly increased (300- to 400-fold) in KU80 knockouts compared to wild-type strains. Target DNA flanks of only approximately 500 bp were found to be sufficient for efficient gene replacements in KU80 knockouts. KU80 knockouts stably retained a normal growth rate in vitro and the high virulence phenotype of type I strains but exhibited an increased sensitivity to double-strand DNA breaks induced by treatment with phleomycin or gamma-irradiation. Collectively, these results revealed that a significant KU-dependent NHEJ DNA repair pathway is present in Toxoplasma gondii. Integration essentially occurs only at the homologous targeted sites in the KU80 knockout background, making this genetic background an efficient host for gene targeting to speed postgenome functional analysis and genetic dissection of parasite biology.
Figures
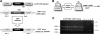
Similar articles
-
Genetic manipulation in Δku80 strains for functional genomic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii.J Vis Exp. 2013 Jul 12;(77):e50598. doi: 10.3791/50598. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23892917 Free PMC article.
-
Tagging of endogenous genes in a Toxoplasma gondii strain lacking Ku80.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Apr;8(4):530-9. doi: 10.1128/EC.00358-08. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19218426 Free PMC article.
-
Ku80 gene is related to non-homologous end-joining and genome stability in Aspergillus niger.Curr Microbiol. 2011 Apr;62(4):1342-6. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9853-5. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Curr Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21225265
-
Type II Toxoplasma gondii KU80 knockout strains enable functional analysis of genes required for cyst development and latent infection.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Sep;10(9):1193-206. doi: 10.1128/EC.00297-10. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 21531875 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Ku80 in microhomology-mediated end joining for DNA double-strand breaks in vivo.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 May 1;6(5):639-48. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 22. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17236818
Cited by
-
Pyrimidine Pathway-Dependent and -Independent Functions of the Toxoplasma gondii Mitochondrial Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase.Infect Immun. 2016 Sep 19;84(10):2974-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00187-16. Print 2016 Oct. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 27481247 Free PMC article.
-
The Toxoplasma effector GRA28 promotes parasite dissemination by inducing dendritic cell-like migratory properties in infected macrophages.Cell Host Microbe. 2022 Nov 9;30(11):1570-1588.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.10.001. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Cell Host Microbe. 2022. PMID: 36309013 Free PMC article.
-
Avirulent uracil auxotrophs based on disruption of orotidine-5'-monophosphate decarboxylase elicit protective immunity to Toxoplasma gondii.Infect Immun. 2010 Sep;78(9):3744-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00287-10. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20605980 Free PMC article.
-
Centrin2 from the human parasite Toxoplasma gondii is required for its invasion and intracellular replication.J Cell Sci. 2019 Jul 1;132(13):jcs228791. doi: 10.1242/jcs.228791. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31182647 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Single-Gene and Gene Family Editing in the Apicomplexan Parasite Eimeria tenella Using CRISPR-Cas9.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Feb 25;8:128. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00128. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32158750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chaudhary, K., B. A. Fox, and D. J. Bzik. 2007. Toxoplasma gondii: the model apicomplexan parasite: perspectives and methods. Elsevier, London, United Kingdom.
-
- Colot, H. V., G. Park, G. E. Turner, C. Ringelberg, C. M. Crew, L. Litvinkova, R. L. Weiss, K. A. Borkovich, and J. C. Dunlap. 2006. A high-throughput gene knockout procedure for Neurospora reveals functions for multiple transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 10310352-10357. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conway, C., R. McCulloch, M. L. Ginger, N. P. Robinson, A. Browitt, and J. D. Barry. 2002. Ku is important for telomere maintenance, but not for differential expression of telomeric VSG genes, in African trypanosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 27721269-21277. - PubMed
-
- Cruz, A., and S. M. Beverley. 1990. Gene replacement in parasitic protozoa. Nature 348171-173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

