Hedgehog signal transduction by Smoothened: pharmacologic evidence for a 2-step activation process
- PMID: 19218434
- PMCID: PMC2642660
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813373106
Hedgehog signal transduction by Smoothened: pharmacologic evidence for a 2-step activation process
Abstract
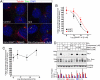
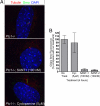
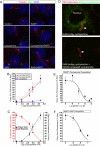
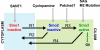
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway controls growth, cell fate decisions, and morphogenesis during development. Damage to Hh transduction machinery can lead to birth defects and cancer. The transmembrane protein Smoothened (Smo) relays the Hh signal and is an important drug target in cancer. Smo enrichment in primary cilia is thought to drive activation of target genes. Using small-molecule agonists and antagonists to dissect Smo function, we find that Smo enrichment in cilia is not sufficient for signaling and a distinct second step is required for full activation. This 2-step mechanism--localization followed by activation--has direct implications for the design and use of anticancer therapeutics targeted against Smo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ. Targeting the Hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:1026–1033. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, McMahon AP, Allen BL. Shifting paradigms in Hedgehog signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Hooper JE, Scott MP. Communicating with Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:306–317. - PubMed
-
- Taipale J, et al. Effects of oncogenic mutations in Smoothened and Patched can be reversed by cyclopamine. Nature. 2000;406:1005–1009. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Tong C, Jiang J. Hedgehog regulates smoothened activity by inducing a conformational switch. Nature. 2007;450:252–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

