Alcohol and injury in the United States general population: a risk function analysis from the 2005 National Alcohol Survey
- PMID: 19219663
- PMCID: PMC2777745
- DOI: 10.1080/10550490802544045
Alcohol and injury in the United States general population: a risk function analysis from the 2005 National Alcohol Survey
Abstract
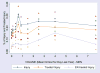
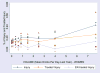
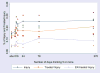
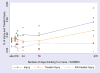
A risk function analysis of data is reported from the 2005 National Alcohol Survey on average daily volume of alcohol and frequency of consuming five or more drinks per day with reporting any injury during the preceding year, an injury that was treated, or an injury that was treated in the emergency room (ER). Data suggest the association of alcohol and injury based on ER studies is not representative of all injuries, and should be taken into account in deriving estimates of risk of injury related to alcohol and alcohol-attributable fractions based on ER studies.
Figures
References
-
- Cherpitel CJ, Bond J, Ye Y. Alcohol and injury: a risk function analysis from the Emergency Room Collaborative Alcohol Analysis Project. Eur Addiction Res. 2006;12:42–52. - PubMed
-
- Cherpitel CJ. Drinking patterns and problems: a comparison of ER patients in an HMO and in the general population. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1992;16(6):1104–1109. - PubMed
-
- Cherpitel CJ. Alcohol consumption and injury in the general population: data from a national sample. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1994;34:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Cherpitel CJ, Tam TW, Midanik LT, Caetano R, Greenfield TK. Alcohol and non-fatal injury in the U.S. general population: a risk function analysis. Accid Anal Prev. 1995;27(5):651–661. - PubMed
-
- Brismar B, Bergman B. The significance of alcohol for violence and accidents. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22(Suppl 7):299S–306S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical