Genetic disorders of surfactant dysfunction
- PMID: 19220077
- PMCID: PMC2987676
- DOI: 10.2350/09-01-0586.1
Genetic disorders of surfactant dysfunction
Abstract
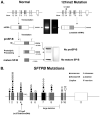
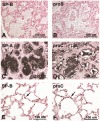
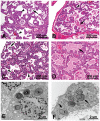
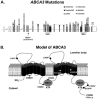
Mutations in the genes encoding the surfactant proteins B and C (SP-B and SP-C) and the phospholipid transporter, ABCA3, are associated with respiratory distress and interstitial lung disease in the pediatric population. Expression of these proteins is regulated developmentally, increasing with gestational age, and is critical for pulmonary surfactant function at birth. Pulmonary surfactant is a unique mixture of lipids and proteins that reduces surface tension at the air-liquid interface, preventing collapse of the lung at the end of expiration. SP-B and ABCA3 are required for the normal organization and packaging of surfactant phospholipids into specialized secretory organelles, known as lamellar bodies, while both SP-B and SP-C are important for adsorption of secreted surfactant phospholipids to the alveolar surface. In general, mutations in the SP-B gene SFTPB are associated with fatal respiratory distress in the neonatal period, and mutations in the SP-C gene SFTPC are more commonly associated with interstitial lung disease in older infants, children, and adults. Mutations in the ABCA3 gene are associated with both phenotypes. Despite this general classification, there is considerable overlap in the clinical and histologic characteristics of these genetic disorders. In this review, similarities and differences in the presentation of these disorders with an emphasis on their histochemical and ultrastructural features will be described, along with a brief discussion of surfactant metabolism. Mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of lung disease caused by mutations in these genes will also be discussed.
Figures






References
-
- Nogee LM. Genetics of the hydrophobic surfactant proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1408:323–333. - PubMed
-
- Whitsett JA, Weaver TE. Hydrophobic surfactant proteins in lung function and disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:2141–2148. - PubMed
-
- Nogee LM. Genetic mechanisms of surfactant deficiency. Biol Neonate. 2004;85:314–318. - PubMed
-
- Nogee LM. Alterations in SP-B and SP-C expression in neonatal lung disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 2004;66:601–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

