Functional interplay between viral and cellular SR proteins in control of post-transcriptional gene regulation
- PMID: 19220464
- PMCID: PMC7164074
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06894.x
Functional interplay between viral and cellular SR proteins in control of post-transcriptional gene regulation
Abstract
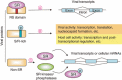
Viruses take advantage of cellular machineries to facilitate their gene expression in the host. SR proteins, a superfamily of cellular precursor mRNA splicing factors, contain a domain consisting of repetitive arginine/serine dipeptides, termed the RS domain. The authentic RS domain or variants can also be found in some virus-encoded proteins. Viral proteins may act through their own RS domain or through interaction with cellular SR proteins to facilitate viral gene expression. Numerous lines of evidence indicate that cellular SR proteins are important for regulation of viral RNA splicing and participate in other steps of post-transcriptional viral gene expression control. Moreover, viral infection may alter the expression levels or modify the phosphorylation status of cellular SR proteins and thus perturb cellular precursor mRNA splicing. We review our current understanding of the interplay between virus and host in post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression via RS domain-containing proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serine-arginine protein kinases and their targets in viral infection and their inhibition.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 May 17;80(6):153. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04808-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37198350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conserved proline-directed phosphorylation regulates SR protein conformation and splicing function.Biochem J. 2015 Mar 1;466(2):311-22. doi: 10.1042/BJ20141373. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 25529026 Free PMC article.
-
SR proteins and related factors in alternative splicing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;623:107-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77374-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18380343 Review.
-
Effects of RNA splicing and post-transcriptional regulation on HIV-1 growth: a quantitative and integrated perspective.Syst Biol (Stevenage). 2005 Sep;152(3):138-52. doi: 10.1049/ip-syb:20050004. Syst Biol (Stevenage). 2005. PMID: 16986277
-
Phosphorylation of the ASF/SF2 RS domain affects both protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions and is necessary for splicing.Genes Dev. 1997 Feb 1;11(3):334-44. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.3.334. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9030686
Cited by
-
Human papillomavirus type 1 E1^E4 protein is a potent inhibitor of the serine-arginine (SR) protein kinase SRPK1 and inhibits phosphorylation of host SR proteins and of the viral transcription and replication regulator E2.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(21):12599-611. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02029-14. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25142587 Free PMC article.
-
SR/RS Motifs as Critical Determinants of Coronavirus Life Cycle.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Aug 21;7:219. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00219. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32974389 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear export and import of human hepatitis B virus capsid protein and particles.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Oct 28;6(10):e1001162. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001162. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 21060813 Free PMC article.
-
NP1 Protein of the Bocaparvovirus Minute Virus of Canines Controls Access to the Viral Capsid Genes via Its Role in RNA Processing.J Virol. 2015 Dec 4;90(4):1718-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02618-15. Print 2016 Feb 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26637456 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant Splicing Events and Epigenetics in Viral Oncogenomics: Current Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2021 Jan 26;10(2):239. doi: 10.3390/cells10020239. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33530521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hertel KJ & Graveley BR (2005) RS domains contact the pre‐mRNA throughout spliceosome assembly. Trends Biochem Sci 30, 115–118. - PubMed
-
- Stamm S (2008) Regulation of alternative splicing by reversible protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 283, 1223–1227. - PubMed
-
- Lin S & Fu XD (2007) SR proteins and related factors in alternative splicing. Adv Exp Med Biol 623, 107–122. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Reddy B & Manley JL (2006) PP1/PP2A phosphatases are required for the second step of pre‐mRNA splicing and target specific snRNP proteins. Mol Cell 23, 819–829. - PubMed
-
- Fluhr R (2008) Regulation of splicing by protein phosphorylation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 326, 119–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

