Neurobehavioral abnormalities in the dysbindin-1 mutant, sandy, on a C57BL/6J genetic background
- PMID: 19220483
- PMCID: PMC2774142
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2009.00477.x
Neurobehavioral abnormalities in the dysbindin-1 mutant, sandy, on a C57BL/6J genetic background
Abstract
Sandy mice have a deletion mutation in the gene encoding dysbindin-1, Dtnbp1, with consequent reduction of the protein in heterozygotes and its loss in homozygotes. The sandy mouse thus serves as an animal model of dysbindin-1 function. As this protein is concentrated in synaptic tissue and affects transmitter release, it may affect neuronal processes that mediate behavior. To investigate the neurobehavioral effects of the Dtnbp1 mutation, we studied littermate sandy and wild-type controls on a C57BL/6J genetic background. The three animal groups were indistinguishable in their external physical characteristics, sensorimotor skills and indices of anxiety-like behaviors. In the open field, however, homozygous animals were hyperactive and appeared to show less habituation to the initially novel environment. In the Morris water maze, homozygous animals displayed clear deficits in spatial learning and memory with marginal deficits in visual association learning. Apart from the last mentioned deficits, these abnormalities are consistent with hippocampal dysfunction and in some cases with elevated dopaminergic transmission via D2 dopamine receptors. As similar deficits in spatial learning and memory have been found in schizophrenia, where decreased dysbindin-1 has been found in the hippocampus, the sandy mouse may also model certain aspects of cognition and behavior relevant to schizophrenia.
Figures

 ), and sdy/sdy (■) mice. ** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.0001. The amount of time expected in the center field by chance (42s) is larger than the observed times.
), and sdy/sdy (■) mice. ** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.0001. The amount of time expected in the center field by chance (42s) is larger than the observed times.
 ), and sdy/sdy (
), and sdy/sdy ( ) mice. No significant differences among groups were found.
) mice. No significant differences among groups were found.
 ) and sdy/sdy mice (■). **Difference at p = 0.002
) and sdy/sdy mice (■). **Difference at p = 0.002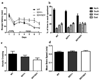
 ), and sdy/sdy (
), and sdy/sdy ( ) mice, (b) percentage of time spent in all quadrants during probe trial, (c) annulus crossings during probe trial soon after final hidden platform trial for WT (■), sdy/+ (
) mice, (b) percentage of time spent in all quadrants during probe trial, (c) annulus crossings during probe trial soon after final hidden platform trial for WT (■), sdy/+ ( ), and sdy/sdy (□) mice, and (d) average swim speed during the probe trial for WT mice (■), sdy/+ (
), and sdy/sdy (□) mice, and (d) average swim speed during the probe trial for WT mice (■), sdy/+ ( ), and sdy/sdy mice (□).
), and sdy/sdy mice (□).References
-
- Allegretti M, Moriconi A, Beccari AR, Di Bitondo R, Bizzarri C, Bertini R, Colotta F. Targeting C5a: recent advances in drug discovery. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12:217–236. - PubMed
-
- Allen NC, Bagade S, McQueen MB, Ioannidis JPA, Kavvoura FK, Khoury MJ, Tanzi RE, Bertram L. Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the SzGene database. Nat Genet. 2008;40:827–834. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SE, Carlson GC, Talbot K, Novak EK, Swank RT, Coulter DA. Failure of inhibition in the hippocampus of the dysbindin mutant “sandy” mouse; Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting; Washington, DC. 2005. Abstract 936.13 from 2005.
-
- Askari BS, Bhardwaj SK, Srivastava LK. Behavioral impairments in dysbindin-deficient sandy mice; Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting; San Diego, CA. 2007. (Abstract 59.1 from 2007)
-
- Bast T, Zhang W-N, Heidbreder C, Feldon J. Hyperactivity and disruption of prepulse inhibition induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate stimulation of the ventral hippocampus and the effects of pretreatment with haloperidol and clozapine. Neuroscience. 2001;103:325–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

