Intrinsic disorder in Viral Proteins Genome-Linked: experimental and predictive analyses
- PMID: 19220875
- PMCID: PMC2649914
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-6-23
Intrinsic disorder in Viral Proteins Genome-Linked: experimental and predictive analyses
Abstract
Background: VPgs are viral proteins linked to the 5' end of some viral genomes. Interactions between several VPgs and eukaryotic translation initiation factors eIF4Es are critical for plant infection. However, VPgs are not restricted to phytoviruses, being also involved in genome replication and protein translation of several animal viruses. To date, structural data are still limited to small picornaviral VPgs. Recently three phytoviral VPgs were shown to be natively unfolded proteins.
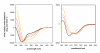
Results: In this paper, we report the bacterial expression, purification and biochemical characterization of two phytoviral VPgs, namely the VPgs of Rice yellow mottle virus (RYMV, genus Sobemovirus) and Lettuce mosaic virus (LMV, genus Potyvirus). Using far-UV circular dichroism and size exclusion chromatography, we show that RYMV and LMV VPgs are predominantly or partly unstructured in solution, respectively. Using several disorder predictors, we show that both proteins are predicted to possess disordered regions. We next extend theses results to 14 VPgs representative of the viral diversity. Disordered regions were predicted in all VPg sequences whatever the genus and the family.
Conclusion: Based on these results, we propose that intrinsic disorder is a common feature of VPgs. The functional role of intrinsic disorder is discussed in light of the biological roles of VPgs.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Protein-RNA linkage and post-translational modifications of two sobemovirus VPgs.J Gen Virol. 2011 Feb;92(Pt 2):445-52. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.026476-0. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Gen Virol. 2011. PMID: 21068217
-
Virulence domain of the RYMV genome-linked viral protein VPg towards rice rymv1-2-mediated resistance.Arch Virol. 2008;153(6):1161-4. doi: 10.1007/s00705-008-0087-9. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Arch Virol. 2008. PMID: 18421414
-
Potato virus A genome-linked protein VPg is an intrinsically disordered molten globule-like protein with a hydrophobic core.Virology. 2008 Aug 1;377(2):280-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.04.025. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18533220 Free PMC article.
-
The biogeography of viral emergence: rice yellow mottle virus as a case study.Curr Opin Virol. 2015 Feb;10:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Curr Opin Virol. 2015. PMID: 25544357 Review.
-
The genome-linked protein VPg of plant viruses-a protein with many partners.Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Nov;1(5):347-54. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.09.010. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22440836 Review.
Cited by
-
Inherent structural disorder and dimerisation of murine norovirus NS1-2 protein.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030534. Epub 2012 Feb 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347381 Free PMC article.
-
Overview on Sobemoviruses and a Proposal for the Creation of the Family Sobemoviridae.Viruses. 2015 Jun 15;7(6):3076-115. doi: 10.3390/v7062761. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26083319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of mutational robustness of the intrinsically disordered viral protein VPg and of its interactor eIF4E.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 14;14(2):e0211725. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211725. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30763345 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based mutational analysis of eIF4E in relation to sbm1 resistance to pea seed-borne mosaic virus in pea.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 24;6(1):e15873. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015873. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21283665 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsically disordered proteins of viruses: Involvement in the mechanism of cell regulation and pathogenesis.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2020;174:1-78. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2020.03.001. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 32828463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Robaglia C, Caranta C. Translation initiation factors: a weak link in plant RNA virus infection. Trends in Plant Science. 2006;11:40–45. - PubMed
-
- Gao Z, Johansen E, Eyers S, Thomas CL, Noel Ellis TH, Maule AJ. The potyvirus recessive resistance gene, sbm1, identifies a novel role for translation initiation factor eIF4E in cell-to-cell trafficking. Plant J. 2004;40:376–385. - PubMed
-
- Kanyuka K, Druka A, Caldwell DG, Tymon A, Mc Callum N, Waugh R, Adams MJ. Evidence that the recessive bymovirus resistance locus rym4 in barley corresponds to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E gene. Molecular Plant Pathology. 2005;6:449–458. - PubMed
-
- Ruffel S, Dussault MH, Palloix A, Moury B, Bendahmane A, Robaglia C, Caranta C. A natural recessive resistance gene against potato virus Y in pepper corresponds to the eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) Plant J. 2002;32:1067–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

