Celiac disease as a potential cause of idiopathic portal hypertension: a case report
- PMID: 19220902
- PMCID: PMC2649142
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-3-68
Celiac disease as a potential cause of idiopathic portal hypertension: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Idiopathic portal hypertension is a disorder of unknown etiology, clinically characterized by portal hypertension, splenomegaly and anemia secondary to hypersplenism.
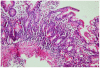
Case presentation: A 54-year-old man was admitted to our hospital for evaluation of malaise, weight loss, abdominal swelling and lower limb edema. His paraclinical tests revealed pancytopenia, large ascites, splenomegaly and esophageal varices consistent with portal hypertension. Duodenal biopsy and serologic findings were compatible with celiac disease. His symptoms improved on a gluten-free diet, but his clinical course was further complicated with ulcerative jejunoileitis, and intestinal T-cell lymphoma.
Conclusion: It seems that celiac disease, by an increased immune reaction in the splenoportal axis, can result in the development of idiopathic portal hypertension in susceptible affected patients.
Figures
References
-
- M'saddek F, Gaha K, Ben Hammouda R, Ben Abdelhafidh N, Bougrine F, Battikh R, Louzir B, Bouali R, Bouzayane A, Othmani S. Idiopathic portal hypertension associated with celiac disease: one case. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2007;31:869–871. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources