A critical role of eEF-2K in mediating autophagy in response to multiple cellular stresses
- PMID: 19221463
- PMCID: PMC2756538
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.5.3.7762
A critical role of eEF-2K in mediating autophagy in response to multiple cellular stresses
Abstract
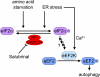
The phosphorylation of the subunit alpha of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2alpha), a critical regulatory event in controlling protein translation, has recently been found to mediate the induction of autophagy. However, the mediators of autophagy downstream of eIF2alpha remain unknown. Here, we provide evidence that eIF2alpha phosphorylation is required for phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF-2) during nutrient starvation. In addition, we show that eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF-2K) is also required for autophagy signaling during ER stress, suggesting that phosphorylation of eEF-2 may serve as an integrator of various cell stresses for autophagy signaling. On the other hand, although the activation of eEF-2K in response to starvation requires the phosphorylation of eIF2alpha, additional pathways relying partly on Ca(2+) flux may control eEF-2K activity during ER stress, as eIF2alpha phosphorylation is dispensable for both eEF-2 phosphorylation and autophagy in this context.
Figures


References
-
- Wek RC, Jiang HY, Anthony TG. Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Hinnebusch A. Mechanism and Regulation of Initiator Methionyl-tRNA Binding to Ribosomes. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Mathews MB, editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor: 2000. pp. 185–244.
-
- Fernandez J, Yaman I, Merrick WC, Koromilas A, Wek RC, Sood R, et al. Regulation of internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation by eukaryotic initiation factor-2α phosphorylation and translation of a small upstream open reading frame. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2050–2058. - PubMed
-
- Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek R, Schapira M, et al. Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 2000;6:1099–1108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
