Benzo[e]pyridoindoles, novel inhibitors of the aurora kinases
- PMID: 19221479
- PMCID: PMC3325905
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.8.5.7879
Benzo[e]pyridoindoles, novel inhibitors of the aurora kinases
Abstract
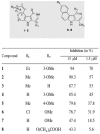
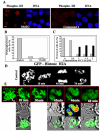
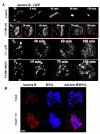
Aurora kinases are serine/threonine protein kinases that are involved in cancer development and are important targets for cancer therapy. By high throughput screening of a chemical library we found that benzo[e]pyridoindole derivatives inhibited Aurora kinase. The most potent compound (compound 1) was found to be an ATP competitive inhibitor, which inhibited in vitro Aurora kinases at the nanomolar range. It prevented, ex vivo, the phosphorylation of Histone H3, induced mitosis exit without chromosome segregation, known phenomena observed upon Aurora B inactivation. This compound was also shown to affect the localization of Aurora B, since in the presence of the inhibitor the enzyme was delocalized on the whole chromosomes and remained associated with the chromatin of newly formed nuclei. In addition, compound 1 inhibited the growth of different cell lines derived from different carcinoma. Its IC(50) for H358 NSCLC (Non Small Cancer Lung Cells), the most sensitive cell line, was 145 nM. Furthermore compound 1 was found to be efficient towards multicellular tumor spheroid growth. It exhibited minimal toxicity in mice while it had some potency towards aggressive NSCLC tumors. Benzo[e]pyridoindoles represent thus a potential new lead for the development of Aurora kinase inhibitors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of an Aurora kinase inhibitor specific for the Aurora B isoform.Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;73(2):716-24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2784. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23117881 Free PMC article.
-
Biological characterization of TAK-901, an investigational, novel, multitargeted Aurora B kinase inhibitor.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Apr;12(4):460-70. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0657. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23358665
-
BPR1K653, a novel Aurora kinase inhibitor, exhibits potent anti-proliferative activity in MDR1 (P-gp170)-mediated multidrug-resistant cancer cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023485. Epub 2011 Aug 24. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887256 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora-B kinase inhibitors for cancer chemotherapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008 Dec;8(14):1514-25. doi: 10.2174/138955708786786480. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 19075809 Review.
-
Aurora B: a new prognostic marker and therapeutic target in cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2011;18(4):482-96. doi: 10.2174/092986711794480203. Curr Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21143115 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro high throughput screening, what next? Lessons from the screening for aurora kinase inhibitors.Biology (Basel). 2014 Feb 27;3(1):167-75. doi: 10.3390/biology3010167. Biology (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24833340 Free PMC article.
-
Unsuccessful mitosis in multicellular tumour spheroids.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):28769-28784. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15673. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28430635 Free PMC article.
-
Basal aurora kinase B activity is sufficient for histone H3 phosphorylation in prophase.Biol Open. 2013 Feb 14;2(4):379-86. doi: 10.1242/bio.20133079. Print 2013 Apr 15. Biol Open. 2013. PMID: 23616922 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of benzo[e]pyridoindolones as kinase inhibitors that disrupt mitosis exit while erasing AMPK-Thr172 phosphorylation on the spindle.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 8;6(26):22152-66. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4158. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26247630 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MELK in tumor cells and tumor microenvironment: from function and mechanism to therapeutic application.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Mar;27(3):887-900. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03664-5. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39187643 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
