Logic of a mammalian metabolic cycle: an oscillated NAD+/NADH redox signaling regulates coordinated histone expression and S-phase progression
- PMID: 19221488
- PMCID: PMC4487625
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.8.5.7880
Logic of a mammalian metabolic cycle: an oscillated NAD+/NADH redox signaling regulates coordinated histone expression and S-phase progression
Abstract
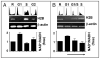
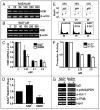
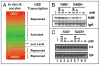
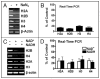
Many biological activities naturally oscillate. Here, we show that the NAD(+)/NADH ratios (redox status) fluctuate during mammalian cell cycle, with the S-phase redox status being the least oxidative. The S-phase NAD(+)/NADH redox status gates histone expression and S-phase progression, and may provide a genome protection mechanism during S-phase DNA replication as implicated in yeast. Accordingly, perturbing the cellular redox inhibits histone expression and leads to S-phase arrest. We propose that the S-phase NAD(+)/NADH redox status constitutes a redox signaling, which along with the cyclin E/cdk2 signaling regulates histone expression and S-phase progression.
Figures

References
-
- Tu BP, Kudlicki A, Rowicka M, McKnight SL. Logic of the yeast metabolic cycle: temporal compartmentalization of cellular processes. Science. 2005;310:1152–8. - PubMed
-
- Tu BP, McKnight SL. Metabolic cycles as an underlying basis of biological oscillations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;9:696–701. - PubMed
-
- Xu Z, Tsurugi K. A potential mechanism of energy-metabolism oscillation in an aerobic chemostat culture of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS J. 2006;273:1696–709. - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Odstrcil EA, Tu B, McKnight SL. Restriction of DNA replication to the reductive phase of the metabolic cycle protects genome integrity. Science. 2007;316:1916–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
