Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs: guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression
- PMID: 19221491
- PMCID: PMC2688687
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.8.6.7907
Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs: guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression
Abstract
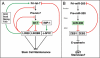
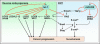
Micro (mi)RNAs are emerging as important regulators of cellular differentiation, their importance underscored by the fact that they are often dysregulated during carcinogenesis. Two evolutionary conserved families, let-7 and miR-200, regulate key differentiation processes during development. Loss of let-7 in cancer results in reverse embryogenesis and dedifferentiation, and miR-200 has been identified as a powerful regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Recent findings have connected let-7 with stem cell maintenance and point at a connection between EMT and stem cell formation. A part of tumor progression can be viewed as a continuum of progressive dedifferentiation (EMT) with a cell at the endpoint that has stem cell-like properties. I propose that steps of this process are driven by specific changes in the expression of let-7 and miR-200 family members.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
The Roles of the Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness.Cells. 2021 Sep 14;10(9):2415. doi: 10.3390/cells10092415. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of Notch in stem cells and cancer.Cancer Lett. 2009 Jun 28;279(1):8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.030. Epub 2008 Nov 20. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 19022563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The reciprocal regulation loop of Notch2 pathway and miR-23b in controlling gastric carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 20;6(20):18012-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4000. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26041881 Free PMC article.
-
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: functional and mechanistic links.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(10):1279-91. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666141211115611. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 25506898 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of an EMT-like transformation and MET in vitro.J Transl Med. 2013 Jul 7;11:164. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-164. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23829659 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping targets exist between the Par-4 and miR-200c axis which regulate EMT and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells.Transl Oncol. 2021 Jan;14(1):100879. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100879. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33045679 Free PMC article.
-
Boswellic acid exerts antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of the let-7 and miR-200 microRNA family.Carcinogenesis. 2012 Dec;33(12):2441-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs286. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22983985 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA gene promoters are frequent targets of aberrant DNA methylation in human breast cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054398. Epub 2013 Jan 16. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342147 Free PMC article.
-
TRIOBP modulates β-catenin signaling by regulation of miR-29b in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Dec 29;81(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05080-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 38157020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cullen BR. Transcription and processing of human microRNA precursors. Mol Cell. 2004;16:861–5. - PubMed
-
- Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Artus CG, Zoller T, Cougot N, Basyuk E, et al. Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 MicroRNA in human cells. Science. 2005;309:1573–6. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
