Pediatric liver transplantation
- PMID: 19222089
- PMCID: PMC2653434
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.648
Pediatric liver transplantation
Abstract
In previous decades, pediatric liver transplantation has become a state-of-the-art operation with excellent success and limited mortality. Graft and patient survival have continued to improve as a result of improvements in medical, surgical and anesthetic management, organ availability, immunosuppression, and identification and treatment of postoperative complications. The utilization of split-liver grafts and living-related donors has provided more organs for pediatric patients. Newer immunosuppression regimens, including induction therapy, have had a significant impact on graft and patient survival. Future developments of pediatric liver transplantation will deal with long-term follow-up, with prevention of immunosuppression-related complications and promotion of as normal growth as possible. This review describes the state-of-the-art in pediatric liver transplantation.
Figures





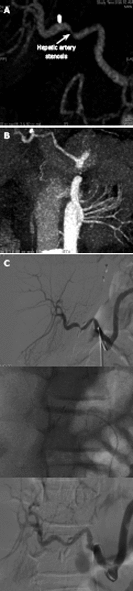
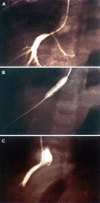

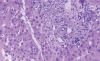
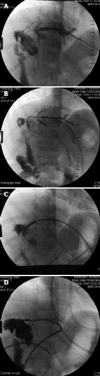
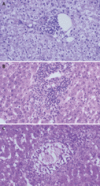

References
-
- McDiarmid SV, Anand R, Lindblad AS. Studies of Pediatric Liver Transplantation: 2002 update. An overview of demographics, indications, timing, and immunosuppressive practices in pediatric liver transplantation in the United States and Canada. Pediatr Transplant. 2004;8:284–294. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman SS, Wood RP, Shaw BW Jr, Markin RS, Gridelli B, Vanderhoof JA. Hepatocarcinoma in a child with the Alagille syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1987;141:698–700. - PubMed
-
- Kayler LK, Rasmussen CS, Dykstra DM, Punch JD, Rudich SM, Magee JC, Maraschio MA, Arenas JD, Campbell DA Jr, Merion RM. Liver transplantation in children with metabolic disorders in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2003;3:334–339. - PubMed
-
- Kemper MJ. The role of preemptive liver transplantation in primary hyperoxaluria type 1. Urol Res. 2005;33:376–379. - PubMed
-
- Kemper MJ. Concurrent or sequential liver and kidney transplantation in children with primary hyperoxaluria type 1? Pediatr Transplant. 2005;9:693–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

