Targeting individual subunits of the FokI restriction endonuclease to specific DNA strands
- PMID: 19223323
- PMCID: PMC2673415
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp046
Targeting individual subunits of the FokI restriction endonuclease to specific DNA strands
Abstract
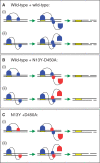
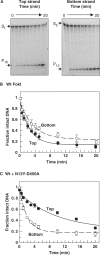
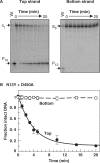
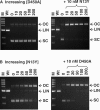
Many restriction endonucleases are dimers that act symmetrically at palindromic DNA sequences, with each active site cutting one strand. In contrast, FokI acts asymmetrically at a non-palindromic sequence, cutting 'top' and 'bottom' strands 9 and 13 nucleotides downstream of the site. FokI is a monomeric protein with one active site and a single monomer covers the entire recognition sequence. To cut both strands, the monomer at the site recruits a second monomer from solution, but it is not yet known which DNA strand is cut by the monomer bound to the site and which by the recruited monomer. In this work, mutants of FokI were used to show that the monomer bound to the site made the distal cut in the bottom strand, whilst the recruited monomer made in parallel the proximal cut in the top strand. Procedures were also established to direct FokI activity, either preferentially to the bottom strand or exclusively to the top strand. The latter extends the range of enzymes for nicking specified strands at specific sequences, and may facilitate further applications of FokI in gene targeting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein assembly and DNA looping by the FokI restriction endonuclease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Mar 23;34(6):1711-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl076. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16556912 Free PMC article.
-
How the BfiI restriction enzyme uses one active site to cut two DNA strands.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 27;100(11):6410-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1131003100. Epub 2003 May 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12750473 Free PMC article.
-
Mva1269I: a monomeric type IIS restriction endonuclease from Micrococcus varians with two EcoRI- and FokI-like catalytic domains.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 16;280(50):41584-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506775200. Epub 2005 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16223716
-
The reaction mechanism of FokI excludes the possibility of targeting zinc finger nucleases to unique DNA sites.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):584-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0390584. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428944 Review.
-
Natural and engineered nicking endonucleases--from cleavage mechanism to engineering of strand-specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(1):1-18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq742. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20805246 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision genome engineering with programmable DNA-nicking enzymes.Genome Res. 2012 Jul;22(7):1327-33. doi: 10.1101/gr.138792.112. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22522391 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating the reaction pathway of the FokI restriction endonuclease by fluorescence resonance energy transfer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(3):1203-13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr809. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21993298 Free PMC article.
-
DNA nicks promote efficient and safe targeted gene correction.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e23981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023981. Epub 2011 Sep 1. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21912657 Free PMC article.
-
Type II restriction endonucleases--a historical perspective and more.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(12):7489-527. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku447. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24878924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA looping by FokI: the impact of twisting and bending rigidity on protein-induced looping dynamics.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jun;40(11):4988-97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks184. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22373924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saenger W. Structure and catalytic function of nucleases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1991;1:130–138.
-
- Yang W, Lee JY, Nowotny M. Making and breaking nucleic acids: two-Mg2+-ion catalysis and substrate specificity. Mol. Cell. 2006;22:5–13. - PubMed
-
- Kelly TJ, Jr., Smith HO. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae II. Base sequence of the recognition site. J. Mol. Biol. 1970;51:393–409. - PubMed
-
- Stoddard BL. Homing endonuclease structure and function. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2005;38:49–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

