First Streptococcus pyogenes signature-tagged mutagenesis screen identifies novel virulence determinants
- PMID: 19223485
- PMCID: PMC2681771
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01306-08
First Streptococcus pyogenes signature-tagged mutagenesis screen identifies novel virulence determinants
Abstract
The virulence of bacterial pathogens is a complex process that requires the dynamic expression of many genes for the pathogens to invade and circumvent host defenses, as well as to proliferate in vivo. In this study, we employed a large-scale screen, signature-tagged mutagenesis (STM), to identify Streptococcus pyogenes virulence genes important for pathogenesis within the host. Approximately 1,200 STM mutants were created and screened using the zebrafish infectious disease model. The transposon insertion site was identified for 29 of the 150 mutants that were considered attenuated for virulence. Previously reported streptococcal virulence genes, such as mga, hasA, amrA, smeZ, and two genes in the sil locus, were identified, confirming the utility of the model for revealing genes important for virulence. Multiple genes not previously implicated in virulence were also identified, including genes encoding putative transporters, hypothetical cytosolic proteins, and macrolide efflux pumps. The STM mutant strains display various levels of attenuation, and multiple separate insertions were identified in either the same gene or the same locus, suggesting that these factors are important for this type of acute, invasive infection. We further examined two such genes, silB and silC of a putative quorum-sensing regulon, and determined that they are significant virulence factors in our model of necrotizing fasciitis. sil locus promoter expression was examined under various in vitro conditions, as well as in zebrafish tissues, and was found to be differentially induced. This study was a unique investigation of S. pyogenes factors required for successful invasive infection.
Figures

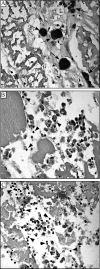
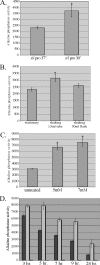

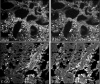
Similar articles
-
A locus of group A Streptococcus involved in invasive disease and DNA transfer.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Oct;46(1):87-99. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03127.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12366833
-
New Pathogenesis Mechanisms and Translational Leads Identified by Multidimensional Analysis of Necrotizing Myositis in Primates.mBio. 2020 Feb 18;11(1):e03363-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03363-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32071274 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Mutagenesis in Borrelia burgdorferi.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1690:201-223. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7383-5_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29032547
-
Signature-tagged mutagenesis: technical advances in a negative selection method for virulence gene identification.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Oct;8(5):612-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2005.08.013. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16126452 Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of necrotizing fasciitis.Annu Rev Pathol. 2010;5:1-31. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102135. Annu Rev Pathol. 2010. PMID: 19737105 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Genes in the Core Genome of the Human Pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes.Sci Rep. 2015 May 21;5:9838. doi: 10.1038/srep09838. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25996237 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology of sil locus in clinical Streptococcus pyogenes strains.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Jun;52(6):2003-10. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00290-14. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24671796 Free PMC article.
-
Use of zebrafish to probe the divergent virulence potentials and toxin requirements of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Dec;5(12):e1000697. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000697. Epub 2009 Dec 18. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 20019794 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus pyogenes genes that promote pharyngitis in primates.JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):e137686. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.137686. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32493846 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the quorum-sensing streptococcal invasion locus (sil).PLoS Pathog. 2009 Nov;5(11):e1000651. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000651. Epub 2009 Nov 6. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19893632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Autret, N., and A. Charbit. 2005. Lessons from signature-tagged mutagenesis on the infectious mechanisms of pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29703-717. - PubMed
-
- Bakleh, M., L. E. Wold, J. N. Mandrekar, W. S. Harmsen, H. H. Dimashkieh, and L. M. Baddour. 2005. Correlation of histopathologic findings with clinical outcome in necrotizing fasciitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 40410-414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

