Introducing nanochemoprevention as a novel approach for cancer control: proof of principle with green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate
- PMID: 19223530
- PMCID: PMC2950093
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3978
Introducing nanochemoprevention as a novel approach for cancer control: proof of principle with green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate
Abstract
Chemoprevention, especially through the use of naturally occurring phytochemicals capable of impeding the process of one or more steps of carcinogenesis process, is a promising approach for cancer management. Despite promising results in preclinical settings, its applicability to humans has met with limited success largely due to inefficient systemic delivery and bioavailability of promising chemopreventive agents. Here, we introduce the concept of nanochemoprevention, which uses nanotechnology for enhancing the outcome of chemoprevention. We encapsulated green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol nanoparticles and observed that encapsulated EGCG retains its biological effectiveness with over 10-fold dose advantage for exerting its proapoptotic and angiogenesis inhibitory effects, critically important determinants of chemopreventive effects of EGCG in both in vitro and in vivo systems. Thus, this study could serve as a basis for the use of nanoparticle-mediated delivery to enhance bioavailability and limit any unwanted toxicity of chemopreventive agents, such as EGCG.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
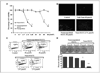
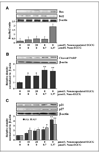
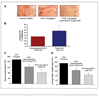
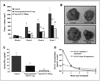
References
-
- Murray CJL, Lopez AD, editors. The global burden of disease: a comprehensive assessment of mortality and disability from diseases, injuries and risk factors in 1990 and projected to 2020. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press on behalf of the World Health Organization and the World Bank; 1996.
-
- Siddiqui IA, Afaq F, Adhami VM, Mukhtar H. Prevention of prostate cancer through custom tailoring of chemopreventive regimen. Chem Biol Interact. 2008;171:122–132. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama N. Nanomedicine: nanocarriers shape up for long life. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:203–204. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Khan N, Afaq F, Saleem M, Ahmad N, Mukhtar H. Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res. 2006;66:2500–2505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

