Changes in insulin sensitivity and insulin release in relation to glycemia and glucose tolerance in 6,414 Finnish men
- PMID: 19223598
- PMCID: PMC2671053
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-1607
Changes in insulin sensitivity and insulin release in relation to glycemia and glucose tolerance in 6,414 Finnish men
Abstract
Objective: We evaluated insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion across the entire range of fasting (FPG) and 2-h plasma glucose (PG), and we investigated the differences in insulin sensitivity and insulin release in different glucose tolerance categories.
Research design and methods: A total of 6,414 Finnish men (aged 57 +/- 7 years, BMI 27.0 +/- 3.9 kg/m2) from our ongoing population-based METSIM (Metabolic Syndrome in Men) study were included. Of these subjects, 2,168 had normal glucose tolerance, 2,859 isolated impaired fasting glucose (IFG), 217 isolated impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), 701 a combination of IFG and IGT, and 469 newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
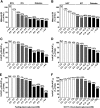
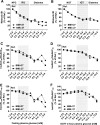
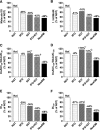
Results: The Matsuda index of insulin sensitivity decreased substantially within the normal range of FPG (-17%) and 2-h PG (-37%) and was approximately -65 and -53% in the diabetic range of FPG and 2-h PG, respectively, compared with the reference range (FPG and 2-h PG <5.0 mmol/l). Early-phase insulin release declined by only approximately -5% within the normal range of FPG and 2-h PG but decreased significantly in the diabetic range of FPG (by 32-70%) and 2-h PG (by 33-51%). Changes in insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in relation to hyperglycemia were independent of obesity. The predominant feature of isolated IGT was impaired peripheral insulin sensitivity. Isolated IFG was characterized by impaired early and total insulin release.
Conclusions: Peripheral insulin sensitivity was already decreased substantially at low PG levels within the normoglycemic range, whereas impairment in insulin secretion was observed mainly in the diabetic range of FPG and 2-h PG. Obesity did not affect changes in insulin sensitivity or insulin secretion in relation to hyperglycemia.
Figures
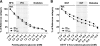
References
-
- Unwin N, Shaw J, Zimmet P, Alberti KG: Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycaemia: the current status on definition and intervention. Diabet Med 2002; 19: 708– 723 - PubMed
-
- Genuth S, Alberti KG, Bennett P, Buse J, Defronzo R, Kahn R, Kitzmiller J, Knowler WC, Lebovitz H, Lernmark A, Nathan D, Palmer J, Rizza R, Saudek C, Shaw J, Steffes M, Stern M, Tuomilehto J, Zimmet P; the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 26: 3160– 3167, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Dunstan DW, Zimmet PZ, Welborn TA, De Courten MP, Cameron AJ, Sicree RA, Dwyer T, Colagiuri S, Jolley D, Knuiman M, Atkins R, Shaw JE: The rising prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance: the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 829– 834 - PubMed
-
- Carnevale Schianca GP, Rossi A, Sainaghi PP, Maduli E, Bartoli E: The significance of impaired fasting glucose versus impaired glucose tolerance: importance of insulin secretion and resistance. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 1333– 1337 - PubMed
-
- Vaccaro O, Riccardi G: Changing the definition of impaired fasting glucose: impact on the classification of individuals and risk definition. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 1786– 1788 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

