Stereotactic radiotherapy for lung cancer using a flattening filter free Clinac
- PMID: 19223837
- PMCID: PMC5720505
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v10i1.2880
Stereotactic radiotherapy for lung cancer using a flattening filter free Clinac
Abstract
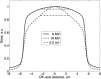
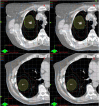
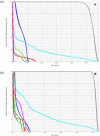
The objective of this study was to assess the feasibility of stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage lung cancer using photon beams from a Varian Clinac accelerator operated without a flattening filter. Treatment plans were generated for 10 lung cancer patients with isolated lesions less than 3 cm in diameter. For each patient, two plans were generated, one with and one without the flattening filter. Plans were generated with Eclipse 8.0 (Varian Medical Systems) commissioned with beam data measured on a Clinac 21EX (Varian Medical Systems) operated with and without the flattening filter. Removal of the flattening filter increased the dose rate. The median beam-on time per field was reduced from 25 sec (with the filter) to 11 sec (without the filter), increasing the feasibility of breath-hold treatments and the efficiency of gated treatments. Differences in a dose heterogeneity index for the planning target volume between plans with flattened and unflattened beams were statistically insignificant. Differences in mean doses to organs at risk were small, typically about 10 cGy over the entire treatment. The study concludes that radiotherapy with unflattened beams is feasible and requires substantially less beam-on time, facilitating breath-hold and gating techniques.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment-planning study of prostate cancer intensity-modulated radiotherapy with a Varian Clinac operated without a flattening filter.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007 Aug 1;68(5):1567-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.04.025. Epub 2007 Jun 4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. PMID: 17544596
-
Dosimetric comparison of flattened and unflattened beams for stereotactic ablative radiotherapy of stage I non-small cell lung cancer.Med Phys. 2014 Mar;41(3):031709. doi: 10.1118/1.4866231. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24593713
-
A simple, yet novel hybrid-dynamic conformal arc therapy planning via flattening filter-free beam for lung stereotactic body radiotherapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020 Jun;21(6):83-92. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12868. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32243704 Free PMC article.
-
Flattening filter free beams in SBRT and IMRT: dosimetric assessment of peripheral doses.Z Med Phys. 2011 May;21(2):91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2010.07.003. Epub 2010 Oct 2. Z Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 20888199
-
Progress and prospects of flattening filter free beam technology in radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021 Jul;163:103396. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103396. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34146680 Review.
Cited by
-
Flattening filter-free accelerators: a report from the AAPM Therapy Emerging Technology Assessment Work Group.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 May 8;16(3):5219. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i3.5219. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26103482 Free PMC article.
-
Improved clinical efficiency in CNS stereotactic radiosurgery using a flattening filter free linear accelerator.J Radiosurg SBRT. 2011;1(2):117-122. J Radiosurg SBRT. 2011. PMID: 29296305 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy with volumetric intensity-modulated arc therapy and flattening filter-free beams: dosimetric considerations.Strahlenther Onkol. 2024 Apr;200(4):346-357. doi: 10.1007/s00066-023-02181-8. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Strahlenther Onkol. 2024. PMID: 38092967 Free PMC article.
-
[Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Small Lesions Applying A Flattening Filter Free Clinac].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 May;18(5):301-7. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.05.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25975301 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A single centre evaluation of the 2019 UK SABR consortium guidelines for primary lung cancer: correlation between Prescription Dose Spillage and inverse Paddick Conformity Index.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022 May 19;27(2):209-214. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2021.0135. eCollection 2022. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022. PMID: 36299394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uematsu M, Shioda A, Tahara K, et al. Focal, high dose, and fractionated modified stereotactic radiation therapy for lung carcinoma patients: a preliminary experience. Cancer. 1998;82(6):1062–70. - PubMed
-
- Uematsu M, Shioda A, Suda A, et al. Computed tomography‐guided frameless stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer: a 5‐year experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51(3):666–70. - PubMed
-
- Wulf J, Haedinger U, Oppitz U, Thiele W, Ness‐Dourdoumas R, Flentje M. Stereotactic radiotherapy of targets in the lung and liver. Strahlenther Onkol 2001;177(12):645–55. - PubMed
-
- Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Aoki T, et al. Clinical outcomes of 3D conformal hypofractionated single high‐dose radiotherapy for one or two lung tumors using a stereotactic body frame. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;52(4):1041–46. - PubMed
-
- Fukumoto S, Shirato H, Shimizu S, et al. Small‐volume image‐guided radiotherapy using hypofractionated, coplanar, and noncoplanar multiple fields for patients with inoperable Stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. Cancer. 2002;95(7):1546–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

