Outcome of a second two-stage reimplantation for periprosthetic knee infection
- PMID: 19224302
- PMCID: PMC2690747
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-009-0739-4
Outcome of a second two-stage reimplantation for periprosthetic knee infection
Abstract
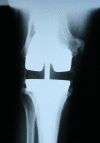
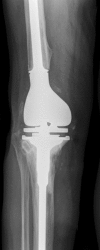
Recurrent or persistent infection after two-stage exchange arthroplasty for previously infected total knee replacement is a challenging clinical situation. We asked whether a second two-stage procedure could eradicate the infection and preserve knee function. We evaluated 18 selected patients with failed two-stage total knee arthroplasty implantation treated with a second two-stage reimplantation between 1999 and 2005. Failure of treatment was defined as recurrence or persistence of infection. The minimum followup was 24 months (mean, 40 months; range, 24-83 months). Recurrent or persistent infection was diagnosed in four of 18 patients, two of whom were successfully treated with a third two-stage exchange arthroplasty. Knee Society score questionnaires administered at the last followup showed an average Knee Society knee score of 73 points (range, 24-100 points) and an average functional score of 49 points (range, 20-90 points). The data suggest repeat two-stage exchange arthroplasty is a reasonable option for eradicating periprosthetic infection, relieving pain, and achieving a satisfactory level of function for some patients.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

