Perioperative dexamethasone does not affect functional outcome in total hip arthroplasty
- PMID: 19224304
- PMCID: PMC2674173
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-009-0733-x
Perioperative dexamethasone does not affect functional outcome in total hip arthroplasty
Abstract
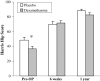
Current trends in orthopaedic surgery have explored different forms of adjuvant treatments to minimize postoperative pain and the risk of nausea and vomiting. A small single preoperative dose of dexamethasone, as part of a comprehensive multimodal analgesic regimen in low-risk patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty (THA), provides antiemetic and opioid-sparing effects but the longer-term effects on pain, complications, or function are not known. We therefore asked whether such a routine would affect longer-term pain, complications, or function. Fifty patients undergoing elective primary THA using spinal anesthesia were initially randomized to receive either dexamethasone (40 mg intravenous) or saline placebo. The patients, anesthesiologists, nurses, and research coordinators were blinded to the study arms. The functional outcome was measured using the Harris hip score. Outcomes were assessed 6 weeks and 1 year postoperatively. We observed no difference in resting pain between the two groups at either time period. Both groups had similar functional outcome scores for the total Harris hip score and individual scoring items at each followup interval. There were no wound complications, deep infections, or osteonecrosis in the contralateral hip at 1-year followup. We recommend the addition of a small single preoperative dose of dexamethasone to a comprehensive multimodal analgesic regimen in low-risk patients given its immediate antiemetic and opioid-sparing effects, and absence of subsequent effects.
Level of evidence: Level II, therapeutic study (prospective comparative study). See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures
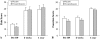
References
-
- Gammer W, Bengtson A, Heideman M. Inhibition of complement activation by high-dose corticosteroids in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;236:205–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

