High-resolution mapping of in vivo gastrointestinal slow wave activity using flexible printed circuit board electrodes: methodology and validation
- PMID: 19224368
- PMCID: PMC4090363
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-009-9654-9
High-resolution mapping of in vivo gastrointestinal slow wave activity using flexible printed circuit board electrodes: methodology and validation
Abstract
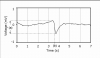
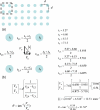
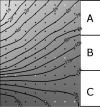
High-resolution, multi-electrode mapping is providing valuable new insights into the origin, propagation, and abnormalities of gastrointestinal (GI) slow wave activity. Construction of high-resolution mapping arrays has previously been a costly and time-consuming endeavor, and existing arrays are not well suited for human research as they cannot be reliably and repeatedly sterilized. The design and fabrication of a new flexible printed circuit board (PCB) multi-electrode array that is suitable for GI mapping is presented, together with its in vivo validation in a porcine model. A modified methodology for characterizing slow waves and forming spatiotemporal activation maps showing slow waves propagation is also demonstrated. The validation study found that flexible PCB electrode arrays are able to reliably record gastric slow wave activity with signal quality near that achieved by traditional epoxy resin-embedded silver electrode arrays. Flexible PCB electrode arrays provide a clinically viable alternative to previously published devices for the high-resolution mapping of GI slow wave activity. PCBs may be mass-produced at low cost, and are easily sterilized and potentially disposable, making them ideally suited to intra-operative human use.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A comparison of gold versus silver electrode contacts for high-resolution gastric electrical mapping using flexible printed circuit board arrays.Physiol Meas. 2011 Mar;32(3):N13-22. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/32/3/N02. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Physiol Meas. 2011. PMID: 21252419 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Electrode Diameter and Contact Material on Signal Morphology of Gastric Bioelectrical Slow Wave Recordings.Ann Biomed Eng. 2020 Apr;48(4):1407-1418. doi: 10.1007/s10439-020-02457-5. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 31980997
-
High-resolution electrical mapping of porcine gastric slow-wave propagation from the mucosal surface.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 May;29(5):10.1111/nmo.13010. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13010. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 28035728 Free PMC article.
-
Electrogastrography: basic knowledge, recording, processing and its clinical applications.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005 Apr;20(4):502-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2004.03751.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. PMID: 15836697 Review.
-
Methods for High-Resolution Electrical Mapping in the Gastrointestinal Tract.IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2019;12:287-302. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2018.2867555. Epub 2018 Aug 29. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 30176605 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies to Refine Gastric Stimulation and Pacing Protocols: Experimental and Modeling Approaches.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 22;15:645472. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.645472. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33967679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improved signal processing techniques for the analysis of high resolution serosal slow wave activity in the stomach.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011;2011:1737-40. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6090497. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011. PMID: 22254662 Free PMC article.
-
A framework for the online analysis of multi-electrode gastric slow wave recordings.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011;2011:1741-4. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6090498. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011. PMID: 22254663 Free PMC article.
-
Electrogastrography measurement systems and analysis methods used in clinical practice and research: comprehensive review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 1;11:1369753. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1369753. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39011457 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of surgical excisions on human gastric slow wave conduction, defined by high-resolution electrical mapping and in silico modeling.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015 Oct;27(10):1409-22. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12637. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015. PMID: 26251163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behm B, Stollman N. Postoperative ileus: etiologies and interventions. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003;1:71–80. doi:10.1053/cgh.2003.50012. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw LA, Irimia A, Sims JA, Gallucci MR, Palmer RL, Richards WO. Biomagnetic characterization of spatiotemporal parameters of the gastric slow wave. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006 Aug;18(8):619–31. - PubMed
-
- Buist ML, Cheng LK, Yassi R, Bradshaw LA, Richards WO, Pullan AJ. An anatomical model of the gastric system for producing bioelectric and biomagnetic fields. Physiol. Meas. 2004;25:849–861. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/25/4/006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

