Lowering blood pressure reduces renal events in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 19225038
- PMCID: PMC2663832
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008070667
Lowering blood pressure reduces renal events in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
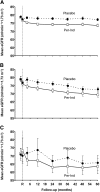
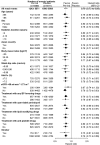
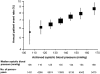
BP is an important determinant of kidney disease among patients with diabetes. The recommended thresholds to initiate treatment to lower BP are 130/80 and 125/75 mmHg for people with diabetes and nephropathy, respectively. We sought to determine the effects of lowering BP below these currently recommended thresholds on renal outcomes among 11,140 patients who had type 2 diabetes and participated in the Action in Diabetes and Vascular disease: preterAx and diamicroN-MR Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) study. Patients were randomly assigned to fixed combination perindopril-indapamide or placebo, regardless of their BP at entry. During a mean follow-up of 4.3 yr, active treatment reduced the risk for renal events by 21% (P < 0.0001), which was driven by reduced risks for developing microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria (both P < 0.003). Effects of active treatment were consistent across subgroups defined by baseline systolic or diastolic BP. Lower systolic BP levels during follow-up, even to <110 mmHg, was associated with progressively lower rates of renal events. In conclusion, BP-lowering treatment with perindopril-indapamide administered routinely to individuals with type 2 diabetes provides important renoprotection, even among those with initial BP <120/70 mmHg. We could not identify a BP threshold below which renal benefit is lost.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00145925.
Figures

References
-
- US Renal Data System: USRDS Annual Data Report, Bethesda, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2007
-
- Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR: Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: The United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int 63: 225–232, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Ritz E, Orth SR: Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 341: 1127–1133, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Ravid M, Brosh D, Levi Z, Bar-Dayan Y, Ravid D, Rachmani R: Use of enalapril to attenuate decline in renal function in normotensive, normoalbuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 128: 982–988, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, Bruno S, Iliev IP, Brusegan V, Rubis N, Gherardi G, Arnoldi F, Ganeva M, Ene-Iordache B, Gaspari F, Perna A, Bossi A, Trevisan R, Dodesini AR, Remuzzi G: Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 351: 1941–1951, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

