Bloodstream infections due to Trichosporon spp.: species distribution, Trichosporon asahii genotypes determined on the basis of ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer 1 sequencing, and antifungal susceptibility testing
- PMID: 19225102
- PMCID: PMC2668300
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01614-08
Bloodstream infections due to Trichosporon spp.: species distribution, Trichosporon asahii genotypes determined on the basis of ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer 1 sequencing, and antifungal susceptibility testing
Abstract
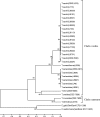
The reevaluation of the genus Trichosporon has led to the replacement of the old taxon Trichosporon beigelii by six new species. Sequencing of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) intergenic spacer 1 (IGS1) is currently mandatory for accurate Trichosporon identification, but it is not usually performed in routine laboratories. Here we describe Trichosporon species distribution and prevalence of Trichosporon asahii genotypes based on rDNA IGS1 sequencing as well as antifungal susceptibility profiles of 22 isolates recovered from blood cultures. The clinical isolates were identified as follows: 15 T. asahii isolates, five Trichosporon asteroides isolates, one Trichosporon coremiiforme isolate, and one Trichosporon dermatis isolate. We found a great diversity of different species causing trichosporonemia, including a high frequency of isolation of T. asteroides from blood cultures that is lower than that of T. asahii only. Regarding T. asahii genotyping, we found that the majority of our isolates belonged to genotype 1 (86.7%). We report the first T. asahii isolate belonging to genotype 4 in South America. Almost 50% of all T. asahii isolates exhibited amphotericin B MICs of >or=2 microg/ml. Caspofungin MICs obtained for all the Trichosporon sp. isolates tested were consistently high (MICs >or= 2 microg/ml). Most isolates (87%) had high MICs for 5-flucytosine, but all of them were susceptible to triazoles, markedly to voriconazole (all MICs <or= 0.06 microg/ml).
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad, S., M. Al-Mahmeed, and Z. U. Khan. 2005. Characterization of Trichosporon species isolated from clinical specimens in Kuwait. J. Med. Microbiol. 54639-646. - PubMed
-
- Asada, N., H. Uryu, M. Koseki, M. Takeuchi, M. Komatsu, and K. Matsue. 2006. Successful treatment of breakthrough Trichosporon asahii fungemia with voriconazole in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 43e39-e41. - PubMed
-
- Barnett, J. A., R. W. Payne, and D. Yarrow. 2000. Yeasts: characteristics and identification, 3rd ed. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
-
- Bayramoglu, G., M. Sonmez, I. Tosun, K. Aydin, and F. Aydin. 2008. Breakthrough Trichosporon asahii fungemia in neutropenic patient with acute leukemia while receiving caspofungin. Infection 3668-70. - PubMed
-
- Biasoli, M. S., D. Carlson, G. J. Chiganer, R. Parodi, A. Greca, M. E. Tosello, A. G. Luque, and A. Montero. 2008. Systemic infection caused by Trichosporon asahii in a patient with liver transplant. Med. Mycol. 46719-723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

