Population differences in associations between C-reactive protein concentration and adiposity: comparison of young adults in the Philippines and the United States
- PMID: 19225115
- PMCID: PMC2667466
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.27080
Population differences in associations between C-reactive protein concentration and adiposity: comparison of young adults in the Philippines and the United States
Abstract
Background: Inflammation may be an important mediator of the association between nutrition and cardiovascular diseases, but most studies have been conducted in Western populations with high rates of overweight and obesity and low levels of infectious disease.
Objectives: This study sought to investigate the predictors of C-reactive protein (CRP) in young adults living in the Philippines and to examine patterns of association with adiposity compared with young adults in the United States.
Design: Maximum likelihood logistic regression models were used to predict elevated high-sensitivity CRP (>3 mg/L) in relation to anthropometric measures of adiposity, symptoms of infectious disease, and proxy measures of pathogen exposure in men and women from the Philippines (n = 1648; age: 20-22 y). Comparative data were drawn from a nationally representative sample in the United States (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; n = 616; age: 19-24 y).
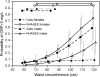
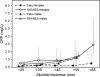
Results: Median concentrations of CRP were substantially lower in the Philippines (0.2 mg/L) than in the United States (0.9 mg/L), and the likelihood of elevated CRP was lower in the Philippines than in the United States at the same level of waist circumference or skinfold thickness. In the Philippines, infectious symptoms and pathogen exposure predicted elevated CRP, independent of adiposity.
Conclusions: Adiposity and infectious exposures are associated with elevated CRP in the Philippines; other populations undergoing comparable lifestyle and dietary changes associated with increasing rates of overweight and obesity are likely experiencing similar double burdens of inflammatory stimuli. Low concentrations of CRP in this Philippine sample raise the question of whether CRP cutoffs based on European or European-American reference populations are appropriate for predicting disease risk in populations undergoing the nutrition transition.
Figures



References
-
- Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2001;286:327–34 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Buring JE, Cook NR, Rifai N. C-reactive protein, the metabolic syndrome, and risk of incident cardiovascular events: an 8-year follow-up of 14 719 initially healthy American women. Circulation 2003;107:391–7 - PubMed
-
- Jenny NS, Yanez ND, Psaty BM, Kuller LH, Hirsch CH, Tracy RP. Inflammation biomarkers and near-term death in older men. Am J Epidemiol 2007;165:684–95 - PubMed
-
- Sattar N, Lowe GD. High sensitivity C-reactive protein and cardiovascular disease: an association built on unstable foundations? Ann Clin Biochem 2006;43:252–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

