Performance of clinical algorithms for HIV-1 diagnosis and antiretroviral initiation among HIV-1-exposed children aged less than 18 months in Kenya
- PMID: 19225401
- PMCID: PMC3223246
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318198a8a4
Performance of clinical algorithms for HIV-1 diagnosis and antiretroviral initiation among HIV-1-exposed children aged less than 18 months in Kenya
Abstract
Background: Ninety percent of HIV-1-infected children live in sub-Saharan Africa. In the absence of diagnosis and antiretroviral therapy, approximately 50% die before 2 years.
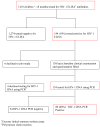
Methods: We evaluated sensitivity and specificity of clinical algorithms for diagnosis of HIV-1 infection and antiretroviral therapy initiation among HIV-1-exposed children aged less than 18 months. Children were identified with routine HIV-1 testing and assessed using 3 sets of criteria: (1) Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (IMCI), (2) World Health Organization Presumptive Diagnosis (WHO-PD) for HIV-1 infection, and (3) CD4 T-lymphocyte cell subsets. HIV-1 infection status was determined using DNA polymerase chain reaction testing.
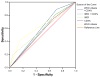
Findings: A total of 1418 children (median age 5.4 months) were screened for HIV-1 antibodies, of whom 144 (10.2%) were seropositive. Of these, 134 (93%) underwent HIV-1 DNA testing and 80 (60%) were found to be HIV-1 infected. Compared with HIV-1 DNA testing, sensitivity and specificity of the IMCI criteria were 19% and 96% and for WHO-PD criteria 43% and 88%, respectively. Inclusion of severe immune deficiency determined by CD4% improved sensitivity of IMCI and WHO-PD criteria to 74% and 84%, respectively; however, specificity declined to 43% and 41%, respectively.
Interpretation: Diagnosis of HIV-1 infection among exposed children less than 18 months in a high-prevalence resource-limited setting remains a challenge, and current recommended algorithms have low sensitivity. This underscores the need for rapid scale-up of viral assays for early infant diagnosis.
Figures

References
-
- Newell ML, Coovadia H, Cortina-Borja M, et al. Mortality of infected and uninfected infants born to HIV infected mothers in Africa: a pooled analysis. Lancet. 2004;364:1236–1243. - PubMed
-
- Sherman GG, Cooper PA, Coovadia AH, Puren AJ, Jones SA, Mokhachane M, Bolton KD. Polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus infection in infants in low resource Settings. Paediatr Infect Dis J. 2005;24:993–997. - PubMed
-
- Zijenah LS, Humphrey J, Nathoo K, Malaba L, Zvandasara P, Mahomva A, Iliff P, Mbizvo MT. Evaluation of the prototype Roche DNA amplification kit incorporating the new SSK145 and SKCC1B Primers in detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA in Zimbabwe. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:3569–3571. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

