Glucose regulates transcription in yeast through a network of signaling pathways
- PMID: 19225458
- PMCID: PMC2657534
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2009.2
Glucose regulates transcription in yeast through a network of signaling pathways
Erratum in
- Mol Syst Biol. 2009;5:257
Abstract
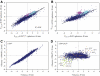
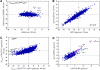
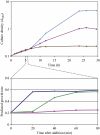
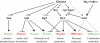
Addition of glucose to yeast cells increases their growth rate and results in a massive restructuring of their transcriptional output. We have used microarray analysis in conjunction with conditional mutations to obtain a systems view of the signaling network responsible for glucose-induced transcriptional changes. We found that several well-studied signaling pathways-such as Snf1 and Rgt-are responsible for specialized but limited responses to glucose. However, 90% of the glucose-induced changes can be recapitulated by the activation of protein kinase A (PKA) or by the induction of PKB (Sch9). Blocking signaling through Sch9 does not interfere with the glucose response, whereas blocking signaling through PKA does. We conclude that both Sch9 and PKA regulate a massive, nutrient-responsive transcriptional program promoting growth, but that they do so in response to different nutritional inputs. Moreover, activating PKA completely recapitulates the transcriptional growth program in the absence of any increase in growth or metabolism, demonstrating that activation of the growth program results solely from the cell's perception of its nutritional status.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Agarwal AK, Rogers PD, Baerson SR, Jacob MR, Barker KS, Cleary JD, Walker LA, Nagle DG, Clark AM (2003) Genome-wide expression profiling of the response to polyene, pyrimidine, azole, and echinocandin antifungal agents in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 278: 34998–35015 - PubMed
-
- Bishop AC, Buzko O, Shokat KM (2001) Magic bullets for protein kinases. Trends Cell Biol 11: 167–172 - PubMed
-
- Boles E, Hollenberg CP (1997) The molecular genetics of hexose transport in yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21: 85–111 - PubMed
-
- Broach JR, Deschenes RJ (1990) The function of ras genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adv Cancer Res 54: 79–139 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

