Reversal of mineral ion homeostasis and soft-tissue calcification of klotho knockout mice by deletion of vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase
- PMID: 19225558
- PMCID: PMC3143194
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2009.24
Reversal of mineral ion homeostasis and soft-tissue calcification of klotho knockout mice by deletion of vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase
Abstract
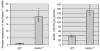
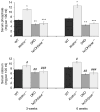
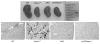
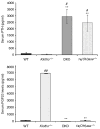
Changes in the expression of klotho, a beta-glucuronidase, contribute to the development of features that resemble those of premature aging, as well as chronic renal failure. Klotho knockout mice have increased expression of the sodium/phosphate cotransporter (NaPi2a) and 1alpha-hydroxylase in their kidneys, along with increased serum levels of phosphate and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. These changes are associated with widespread soft-tissue calcifications, generalized tissue atrophy, and a shorter lifespan in the knockout mice. To determine the role of the increased vitamin D activities in klotho knockout animals, we generated klotho and 1alpha-hydroxylase double-knockout mice. These double mutants regained body weight and developed hypophosphatemia with a complete elimination of the soft-tissue and vascular calcifications that were routinely found in klotho knockout mice. The markedly increased serum fibroblast growth factor 23 and the abnormally low serum parathyroid hormone levels, typical of klotho knockout mice, were significantly reversed in the double-knockout animals. These in vivo studies suggest that vitamin D has a pathologic role in regulating abnormal mineral ion metabolism and soft-tissue anomalies of klotho-deficient mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Ablation of klotho and premature aging: is 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D the key middleman?Kidney Int. 2009 Jun;75(11):1137-1139. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.55. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19444269
References
-
- Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H. Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature. 1997;390:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Tsujikawa H, Kurotaki Y, Fujimori T, et al. Klotho, a gene related to a syndrome resembling human premature aging, functions in a negative regulatory circuit of vitamin D endocrine system. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:2393–2403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

