Synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles stabilized with glycosaminoglycans having distinctive biological activities
- PMID: 19226107
- PMCID: PMC2765565
- DOI: 10.1021/bm801266t
Synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles stabilized with glycosaminoglycans having distinctive biological activities
Abstract
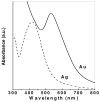
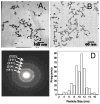
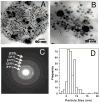
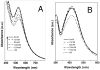
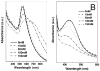
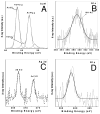
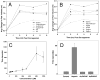
Metal nanoparticles have been studied for their anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory efficacy in various models. Specifically, gold and silver nanoparticles exhibit properties that make these ideal candidates for biological applications. The typical synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles incorporates contaminants that could pose further problems. Here we demonstrate a clean method of synthesizing gold and silver nanoparticles that exhibit biological functions. These nanoparticles were prepared by reducing AuCl(4) and AgNO(3) using heparin and hyaluronan as both reducing and stabilizing agents. The particles show stability under physiological conditions and narrow size distributions for heparin particles and wider distribution for hyaluronan particles. Studies show that the heparin nanoparticles exhibit anticoagulant properties. Additionally, either gold- or silver-heparin nanoparticles exhibit local anti-inflammatory properties without any significant effect on systemic hemostasis upon administration in carrageenan-induced paw edema models. In conclusion, gold and silver nanoparticles complexed with heparin demonstrated effective anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory efficacy, having potential in various local applications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hyaluronan- and heparin-reduced silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2009 Jun;4(4):421-9. doi: 10.2217/nnm.09.24. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19505245 Free PMC article.
-
Gold and silver nanoparticles conjugated with heparin derivative possess anti-angiogenesis properties.Nanotechnology. 2009 Nov 11;20(45):455104. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/45/455104. Epub 2009 Oct 13. Nanotechnology. 2009. PMID: 19822927
-
Anticoagulation and antibacterial properties of heparinized nanosilver with different morphologies.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Aug 15;266:118124. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118124. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 34044940
-
Stabilization of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Preservation and Improvement of Plasmonic Functionalities.Chem Rev. 2019 Jan 9;119(1):664-699. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00341. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 30346757 Review.
-
Structure and anticoagulant properties of sulfated glycosaminoglycans from primitive Chordates.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2002 Mar;74(1):105-12. doi: 10.1590/s0001-37652002000100007. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2002. PMID: 11960179 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel adjuvants & delivery vehicles for vaccines development: a road ahead.Indian J Med Res. 2013 Nov;138(5):779-95. Indian J Med Res. 2013. PMID: 24434331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials for treating cardiovascular diseases: A review.Bioact Mater. 2017 Dec 6;2(4):185-198. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2017.11.002. eCollection 2017 Dec. Bioact Mater. 2017. PMID: 29744429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Cancer and Anti-Inflammatory Potential of the Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles of the Red Sea Sponge Phyllospongia lamellosa Supported by Metabolomics Analysis and Docking Study.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Sep 24;10(10):1155. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10101155. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680736 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-Delivery Silver Nanoparticles: A New Perspective for Phenindione as an Anticoagulant.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 4;11(8):2201. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082201. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626698 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Polysaccharides' Molecular Structure on the Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity of Green Synthesized Composites Based on Silver Nanoparticles and Carboxymethyl-Cellulose.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jun 14;10(6):1164. doi: 10.3390/nano10061164. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Neal DP, Hirsch LR, Halas NJ, Payne JD, West JL. Cancer Lett (Amsterdam, Neth) 2004;209:171–176. - PubMed
-
- Huang X, El-Sayed IH, Qian W, El-Sayed MA. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:2115–2120. - PubMed
-
- Skirtach AG, Dejugnat C, Braun D, Susha AS, Rogach AL, Parak WJ, Moehwald H, Sukhorukov GB. Nano Lett. 2005;5:1371–1377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

