Positive allosteric modulation of the human cannabinoid (CB) receptor by RTI-371, a selective inhibitor of the dopamine transporter
- PMID: 19226282
- PMCID: PMC2697692
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00124.x
Positive allosteric modulation of the human cannabinoid (CB) receptor by RTI-371, a selective inhibitor of the dopamine transporter
Abstract
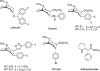
Background and purpose: In our search for an indirect dopamine agonist as therapy for cocaine addiction, several selective inhibitors of the dopamine transporter (DAT), which are 3-phenyltropane analogues, were assayed for their effect on locomotor activity in mice. Interestingly, several of the compounds showed a poor correlation between stimulation of locomotion and DAT inhibition. One of the compounds, 3beta-(4-methylphenyl)-2beta-[3-(4-chlorophenyl)isoxazol-5-yl]tropane (RTI-371), was shown to cross the blood-brain barrier, by binding studies in vivo, and block cocaine-induced locomotor stimulation. As poor pharmacokinetics could not explain the behavioural effects of RTI-371, this compound was screened through our functional assays for activity at other CNS receptors. Initial screening identified RTI-371 as a positive allosteric modulator of the human CB(1) (hCB(1)) receptor.
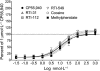
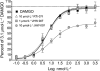
Experimental approach: The effect of RTI-371 and other DAT-selective inhibitors on CP55940-stimulated calcium mobilization was characterized in a calcium mobilization-based functional assay for the hCB(1) receptor. Selected compounds were also characterized in a similar assay for human mu opioid receptor activation to assess the specificity of their effects.
Key results: RTI-371 and several other DAT-selective inhibitors with atypical actions on locomotor behaviour increased the efficacy of CP55940 in a concentration-dependent manner.
Conclusions and implications: These results suggest that the lack of correlation between the DAT-binding affinity and locomotor stimulation of RTI-371 could be due at least in part to its activity as a positive modulator of the hCB(1) receptor.
Figures

References
-
- Agoston GE, Wu JH, Izenwasser S, George C, Katz J, Kline RH, et al. Novel N-substituted 3 alpha-[bis(4′-fluorophenyl)methoxy]tropane analogues: selective ligands for the dopamine transporter. J Med Chem. 1997;40(26):4329–4339. - PubMed
-
- Bergman J, Madras BK, Johnson SE, Spealman RD. Effects of cocaine and related drugs in nonhuman primates. III. Self-administration by squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989;251(1):150–155. - PubMed
-
- Carroll FI, Kotian P, Dehghani A, Gray JL, Kuzemko MA, Parham KA, et al. Cocaine and 3β-(4′-substituted phenyl)tropane-2 beta-carboxylic acid ester and amide analogues. New high-affinity and selective compounds for the dopamine transporter. J Med Chem. 1995;38(2):379–388. - PubMed
-
- Carroll FI, Pawlush N, Kuhar MJ, Pollard GT, Howard JL. Synthesis, monoamine transporter binding properties, and behavioral pharmacology of a series of 3beta-(substituted phenyl)-2beta-(3′-substituted isoxazol-5-yl)tropanes. J Med Chem. 2004a;47(2):296–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

