Pharmacology of ramelteon, a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist: a novel therapeutic drug for sleep disorders
- PMID: 19228178
- PMCID: PMC2871175
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00066.x
Pharmacology of ramelteon, a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist: a novel therapeutic drug for sleep disorders
Abstract
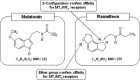
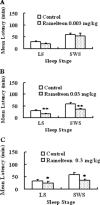
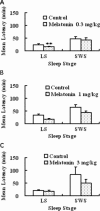
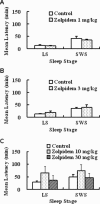
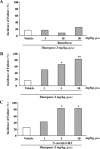
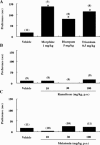
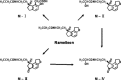
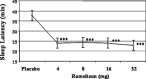
An estimated one-third of the general population is affected by insomnia, and this number is increasing due to more stressful working conditions and the progressive aging of society. However, current treatment of insomnia with hypnotics, gamma-aminobutyric acid A (GABA(A)) receptor modulators, induces various side effects, including cognitive impairment, motor disturbance, dependence, tolerance, hangover, and rebound insomnia. Ramelteon (Rozerem; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Osaka, Japan) is an orally active, highly selective melatonin MT(1)/MT(2) receptor agonist. Unlike the sedative hypnotics that target GABA(A) receptor complexes, ramelteon is a chronohypnotic that acts on the melatonin MT(1) and MT(2) receptors, which are primarily located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus, the body's "master clock." As such, ramelteon possesses the first new therapeutic mechanism of action for a prescription insomnia medication in over three decades. Ramelteon has demonstrated sleep-promoting effects in clinical trials, and coupled with its favorable safety profile and lack of abuse potential or dependence, this chronohypnotic provides an important treatment option for insomnia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
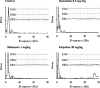
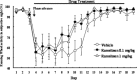
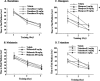
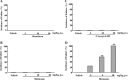
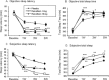
Figures



References
-
- Silber MH. Chronic insomnia. N Engl J Med 2005;353:803–810. - PubMed
-
- Lamberg L. Several sleep disorders reflect gender differences. Psychiatr News 2007;42:40.
-
- Mitler MM. Nonselective and selective benzodiazepine receptor agonists—where are we today? Sleep 2000;23:S39–S47. - PubMed
-
- Roache JD, Griffiths RR. Comparison of triazolam and pentobarbital: performance impairment, subjective effects and abuse ability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1985;234:120–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

