Human cardiac fibroblasts express B-type natriuretic peptide: fluvastatin ameliorates its up-regulation by interleukin-1alpha, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta
- PMID: 19228263
- PMCID: PMC4515057
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00704.x
Human cardiac fibroblasts express B-type natriuretic peptide: fluvastatin ameliorates its up-regulation by interleukin-1alpha, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta
Abstract
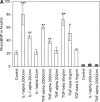
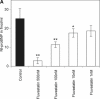
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac hormone, which plays a major role in body fluid and cardiovascular homeostasis. Produced by cardiac ventricles, its expression is highly regulated by various mediators. Canine cardiac fibroblasts have been identified as a source of BNP. Cardiac fibroblasts are key regulators of myocardial structure and function. We treated cultured human adult cardiac fibroblasts (HACF) with 2000 U/ml tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), 200 U/ml interleukin-1alpha (IL-1alpha) or 50 ng/ml transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in the presence or absence of 500 nM fluvastatin. N-terminal pro-BNP (Nt-proBNP) concentration was determined by a competitive enzyme immunoassay. RealTime polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR) was performed to investigate changes in BNP mRNA expression. Nt-proBNP peptide was present in the conditioned media of HACF and incubation with fluvastatin significantly reduced Nt-proBNP peptide levels. Treatment of HACF with TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha or TGF-beta significantly increased Nt-proBNP levels compared with untreated cells. This effect was completely abolished in the presence of fluvastatin. Real-time PCR analysis confirmed these changes at the level of mRNA expression. Our data suggest that cardiac fibroblasts are a potential source of BNP in the human heart. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, associated with ventricular dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis, seem to be major inducers of BNP production in cardiac fibroblasts. This effect can be reverted by a statin. Based on our data, we speculate that elevated plasma BNP levels might not only reflect increased myocardial stretch but also inflammatory and remodelling processes. A possible benefit of statin-induced reduction in BNP production requires further studies.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mechanism of TNFalpha-induced IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 expression in human cardiac fibroblasts: effects of statins and thiazolidinediones.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Oct 1;76(1):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2007.06.003. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17612514
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 expression is regulated by the inflammatory mediators interleukin-1alpha, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, transforming growth factor-beta and oncostatin M in human cardiac myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002 Dec;34(12):1681-91. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2002.2117. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12505065
-
Macrophage colony stimulating factor expression in human cardiac cells is upregulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha via an NF-kappaB dependent mechanism.J Thromb Haemost. 2007 Dec;5(12):2520-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02784.x. Epub 2007 Oct 8. J Thromb Haemost. 2007. PMID: 17922812
-
Essential biochemistry and physiology of (NT-pro)BNP.Eur J Heart Fail. 2004 Mar 15;6(3):257-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2003.12.015. Eur J Heart Fail. 2004. PMID: 14987573 Review.
-
NT-ProBNP: the mechanism behind the marker.J Card Fail. 2005 Jun;11(5 Suppl):S81-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2005.04.019. J Card Fail. 2005. PMID: 15948107 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of putative small molecules for manipulation of enriched signalling pathways in hESC-derived early cardiovascular progenitors by bioinformatics analysis.IET Syst Biol. 2019 Apr;13(2):77-83. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb.2018.5037. IET Syst Biol. 2019. PMID: 33444476 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance is associated with increased concentrations of NT-proBNP in rheumatoid arthritis: IL-6 as a potential mediator.Inflammation. 2014 Jun;37(3):801-8. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9799-4. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24402421 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac gene expression profiling - the quest for an atrium-specific biomarker.Neth Heart J. 2010 Dec;18(12):610-4. doi: 10.1007/s12471-010-0844-8. Neth Heart J. 2010. PMID: 21301625 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective cytokine interleukin-33 is up-regulated by statins in human cardiac tissue.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):6122-6133. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13891. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30216659 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing Myocardial Injury Following Non-Cardiac Surgery: A Potential Role for Preoperative Antioxidant Therapy with Ubiquinone.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 10;10(2):276. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020276. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33579045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jarai R, Wojta J, Huber K. Circulating B-type natriuretic peptides in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Pathophysiological, prognostical and therapeutical considerations. Thromb Haemost. 2005;94:926–32. - PubMed
-
- Hall C. Essential biochemistry and physiology of (NT-pro)BNP. Eur J Heart Fail. 2004;6:257–60. - PubMed
-
- Tsuruda T, Boerrigter G, Huntley BK, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide is produced in cardiac fibroblasts and induces matrix metalloproteinases. Circ Res. 2002;91:1127–34. - PubMed
-
- Manabe I, Shindo T, Nagai R. Gene expression in fibroblasts and fibrosis: involvement in cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 2002;91:1103–13. - PubMed
-
- Bradham WS, Moe G, Wendt KA, et al. TNF-alpha and myocardial matrix metalloproteinases in heart failure: relationship to LV remodeling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282:H1288–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

