Correlational analysis for identifying genes whose regulation contributes to chronic neuropathic pain
- PMID: 19228393
- PMCID: PMC2649910
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-7
Correlational analysis for identifying genes whose regulation contributes to chronic neuropathic pain
Abstract
Background: Nerve injury-triggered hyperexcitability in primary sensory neurons is considered a major source of chronic neuropathic pain. The hyperexcitability, in turn, is thought to be related to transcriptional switching in afferent cell somata. Analysis using expression microarrays has revealed that many genes are regulated in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) following axotomy. But which contribute to pain phenotype versus other nerve injury-evoked processes such as nerve regeneration? Using the L5 spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathy we examined differential changes in gene expression in the L5 (and L4) DRGs in five mouse strains with contrasting susceptibility to neuropathic pain. We sought genes for which the degree of regulation correlates with strain-specific pain phenotype.
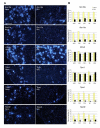
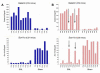
Results: In an initial experiment six candidate genes previously identified as important in pain physiology were selected for in situ hybridization to DRG sections. Among these, regulation of the Na+ channel alpha subunit Scn11a correlated with levels of spontaneous pain behavior, and regulation of the cool receptor Trpm8 correlated with heat hypersensibility. In a larger scale experiment, mRNA extracted from individual mouse DRGs was processed on Affymetrix whole-genome expression microarrays. Overall, 2552 +/- 477 transcripts were significantly regulated in the axotomized L5DRG 3 days postoperatively. However, in only a small fraction of these was the degree of regulation correlated with pain behavior across strains. Very few genes in the "uninjured" L4DRG showed altered expression (24 +/- 28).
Conclusion: Correlational analysis based on in situ hybridization provided evidence that differential regulation of Scn11a and Trpm8 contributes to across-strain variability in pain phenotype. This does not, of course, constitute evidence that the others are unrelated to pain. Correlational analysis based on microarray data yielded a larger "look-up table" of genes whose regulation likely contributes to pain variability. While this list is enriched in genes of potential importance for pain physiology, and is relatively free of the bias inherent in the candidate gene approach, additional steps are required to clarify which transcripts on the list are in fact of functional importance.
Figures


References
-
- Devor M. Response of nerves to injury in relation to neuropathic pain. In: McMahon SL, Koltzenburg M, editor. Wall and Melzack's Textbook of Pain. London: Churchill Livingstone; 2006. pp. 905–927.
-
- Costigan M, Befort K, Karchewski L, Griffin RS, D'Urso D, Allchorne A, Sitarski J, Mannion JW, Pratt RE, Woolf CJ. Replicate high-density rat genome oligonucleotide microarrays reveal hundreds of regulated genes in the dorsal root ganglion after peripheral nerve injury. BMC Neurosci. 2002;3:16–28. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xiao HS, Huang QH, Zhang FX, Bao L, Lu YJ, Guo C, Yang L, Huang WJ, Fu G, Xu SH, Cheng XP, Yan Q, Zhu ZD, Zhang X, Chen Z, Han ZG, Zhang X. Identification of gene expression profile of dorsal root ganglion in the rat peripheral axotomy model of neuropathic pain. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:8360–8365. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Valder CR, Liu JJ, Song YH, Luo ZD. Coupling gene chip analyses and rat genetic variances in identifying potential target genes that may contribute to neuropathic allodynia development. J Neurochem. 2003;87:560–573. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Sun H, Della Penna K, Benz RJ, Xu J, Gerhold DL, Holder DJ, Koblan KS. Chronic neuropathic pain is accompanied by global changes in gene expression and shares pathobiology with neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroscience. 2002;114:529–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

