Association between TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus: a large Human Genome Epidemiology (HuGE) review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 19228405
- PMCID: PMC2653476
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-10-15
Association between TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus: a large Human Genome Epidemiology (HuGE) review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) has been shown to be associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2MD) in multiple ethnic groups in the past two years, but, contradictory results were reported for Chinese and Pima Indian populations. The authors then performed a large meta-analysis of 36 studies examining the association of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with polymorphisms in the TCF7L2 gene in various ethnicities, containing rs7903146 C-to-T (IVS3C>T), rs7901695 T-to-C (IVS3T>C), a rs12255372 G-to-T (IVS4G>T), and rs11196205 G-to-C (IVS4G>C) polymorphisms and to evaluate the size of gene effect and the possible genetic mode of action.
Methods: Literature-based searching was conducted to collect data and three methods, that is, fixed-effects, random-effects and Bayesian multivariate mete-analysis, were performed to pool the odds ratio (OR). Publication bias and study-between heterogeneity were also examined.
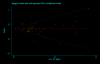
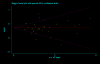
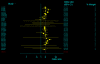
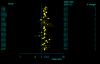
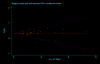
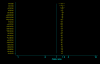
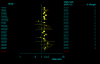
Results: The studies included 35,843 cases of T2DM and 39,123 controls, using mainly primary data. For T2DM and IVS3C>T polymorphism, the Bayesian OR for TT homozygotes and TC heterozygotes versus CC homozygote was 1.968 (95% credible interval (CrI): 1.790, 2.157), 1.406 (95% CrI: 1.341, 1.476), respectively, and the population attributable risk (PAR) for the TT/TC genotypes of this variant is 16.9% for overall. For T2DM and IVS4G>T polymorphism, TT homozygotes and TG heterozygotes versus GG homozygote was 1.885 (95%CrI: 1.698, 2.088), 1.360 (95% CrI: 1.291, 1.433), respectively. Four ORs among these two polymorphisms all yielded significant between-study heterogeneity (P < 0.05) and the main source of heterogeneity was ethnic differences. Data also showed significant associations between T2DM and the other two polymorphisms, but with low heterogeneity (P > 0.10). Pooled ORs fit a codominant, multiplicative genetic model for all the four polymorphisms of TCF7L2 gene, and this model was also confirmed in different ethnic populations when stratification of IVS3C>T and IVS4G>T polymorphisms except for Africans, where a dominant, additive genetic mode is suggested for IVS3C>T polymorphism.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis demonstrates that four variants of TCF7L2 gene are all associated with T2DM, and indicates a multiplicative genetic model for all the four polymorphisms, as well as suggests the TCF7L2 gene involved in near 1/5 of all T2MD. Potential gene-gene and gene-environmental interactions by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene influence the risk of T2MD need further exploration.
Figures




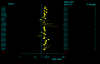






References
-
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:S5–S10. - PubMed
-
- Grant SF, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J, Helgason A, Stefansson H, Emilsson V, Helgadottir A, Styrkarsdottir U, Magnusson KP, Walters GB, Palsdottir E, Jonsdottir T, Gudmundsdottir T, Gylfason A, Saemundsdottir J, Wilensky RL, Reilly MP, Rader DJ, Bagger Y, Christiansen C, Gudnason V, Sigurdsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Gulcher JR, Kong A, Stefansson K. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2006;38:320–323. - PubMed
-
- King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH. Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:1414–1431. - PubMed
-
- Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Ceesay MM, Morgan MW, Kamanda MO, Willoughby VR, Lisk DR. Prevalence of diabetes in rural and urban populations in southern Sierra Leone: a preliminary survey. Trop Med Int Health. 1997;2:272–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

