Point mutation of tyrosine 759 of the IL-6 family cytokine receptor, gp130, augments collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice
- PMID: 19228423
- PMCID: PMC2652421
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-23
Point mutation of tyrosine 759 of the IL-6 family cytokine receptor, gp130, augments collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice
Abstract
Background: Knock-in mice (gp130F759) with a Y759F point mutation in gp130, a signal transducing receptor subunit shared by members of the IL-6 cytokine family, show sustained activation of STAT3, enhanced acute-phase or immune responses, and autoimmune arthritis. We conducted a detailed analysis of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in gp130F759 with a DBA/1J background (D/J.gp130F759).
Methods: We backcrossed gp130F759 to C57BL/6 and DBA/1J, and compared the pathologic changes, including occurrence of arthritis, in the two distinct genetic backgrounds. We analyzed CIA in D/J.gp130F759 and investigated the effects of methotrexate (MTX) on CIA.
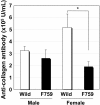
Results: C57BL/6 background gp130F759 mice, but not D/J.gp130F759, spontaneously developed polyarthritis and glomerulonephritis. On the other hand, keratitis of the eyes only developed in D/J.gp130F759, indicating the influence of genetic background on disease development in gp130F759 mice. Resistance of the DBA/1J background against spontaneous arthritis urged us to examine CIA in D/J.gp130F759. CIA in D/J.gp130F759 was more severe, with greater bone destruction, than the control mice. After collagen immunization, splenomegaly and serum levels of rheumatoid factor and anti-DNA antibody were augmented in D/J.gp130F759. Bio-Plex analysis of serum cytokines revealed increased IL-12p40 and PDGF-BB before immunization, and increased levels of IFN-gamma, IL-17, TNF-alpha, IL-9, and MIP-1beta 8 days after the booster dose. IL-6 and PDGF-BB in D/J.gp130F759 showed distinct kinetics from the other cytokines; higher levels were observed after arthritis development. MTX partially attenuated the development of arthritis and inhibited bone destruction in D/J.gp130F759, with reduction of anti-type II collagen antibody levels, suggesting that MTX mainly affects antigen-specific immune responses in CIA.
Conclusion: The Tyr-759 point mutation of the IL-6 family cytokine receptor subunit, gp130, caused autoimmune disease, and this was also influenced by the genetic background. CIA in D/J.gp130F759 is useful for evaluating drugs in a relatively short period because sustained activation of STAT3 may enhance the disease symptoms.
Figures

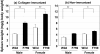
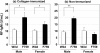
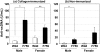



References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Liew FY. Cytokine networks-towards new therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2005;1:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T. Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;16:249–284. - PubMed
-
- Hirano T, Taga T, Yasukawa K, Nakajima K, Nakano N, Takatsuki F, Shimizu M, Murashima A, Tsunasawa S, Sakiyama F, Kishimoto T. Human B-cell differentiation factor defined by an anti-peptide antibody and its possible role in autoantibody production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84:228–231. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

