Estimation of the warfarin dose with clinical and pharmacogenetic data
- PMID: 19228618
- PMCID: PMC2722908
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0809329
Estimation of the warfarin dose with clinical and pharmacogenetic data
Erratum in
- N Engl J Med. 2009 Oct 15;361(16):1613. Dosage error in article text
Abstract
Background: Genetic variability among patients plays an important role in determining the dose of warfarin that should be used when oral anticoagulation is initiated, but practical methods of using genetic information have not been evaluated in a diverse and large population. We developed and used an algorithm for estimating the appropriate warfarin dose that is based on both clinical and genetic data from a broad population base.
Methods: Clinical and genetic data from 4043 patients were used to create a dose algorithm that was based on clinical variables only and an algorithm in which genetic information was added to the clinical variables. In a validation cohort of 1009 subjects, we evaluated the potential clinical value of each algorithm by calculating the percentage of patients whose predicted dose of warfarin was within 20% of the actual stable therapeutic dose; we also evaluated other clinically relevant indicators.
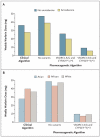
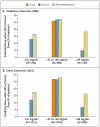
Results: In the validation cohort, the pharmacogenetic algorithm accurately identified larger proportions of patients who required 21 mg of warfarin or less per week and of those who required 49 mg or more per week to achieve the target international normalized ratio than did the clinical algorithm (49.4% vs. 33.3%, P<0.001, among patients requiring < or = 21 mg per week; and 24.8% vs. 7.2%, P<0.001, among those requiring > or = 49 mg per week).
Conclusions: The use of a pharmacogenetic algorithm for estimating the appropriate initial dose of warfarin produces recommendations that are significantly closer to the required stable therapeutic dose than those derived from a clinical algorithm or a fixed-dose approach. The greatest benefits were observed in the 46.2% of the population that required 21 mg or less of warfarin per week or 49 mg or more per week for therapeutic anticoagulation.
2009 Massachusetts Medical Society
Figures
Comment in
-
Pharmacogenetics--tailoring treatment for the outliers.N Engl J Med. 2009 Feb 19;360(8):811-3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe0810630. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19228625 No abstract available.
-
Warfarin pharmacogenetics.N Engl J Med. 2009 Jun 4;360(23):2474; author reply 2475. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc090579. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19494226 No abstract available.
-
Warfarin pharmacogenetics.N Engl J Med. 2009 Jun 4;360(23):2474-5; author reply 2475. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19504712 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wysowski DK, Nourjah P, Swartz L. Bleeding complications with warfarin use: a prevalent adverse effect resulting in regulatory action. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167:1414–9. - PubMed
-
- Budnitz DS, Shehab N, Kegler SR, Richards CL. Medication use leading to emergency department visits for adverse drug events in older adults. Ann Intern Med. 2007;147:755–65. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JL, Horne BD, Stevens SM, et al. Randomized trial of genotype-guided versus standard warfarin dosing in patients initiating oral anticoagulation. Circulation. 2007;116:2563–70. - PubMed
-
- Aquilante CL, Langaee TY, Lopez LM, et al. Influence of coagulation factor, vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1, and cytochrome P450 2C9 gene polymorphisms on warfarin dose requirements. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;79:291–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24 GM061374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM063340/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM032165/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM074492/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068797/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G0800792/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS053646/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL068834/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066176/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL070936/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008692/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 077011/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS045598/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
