Reduced incidence and delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic diseases in growth hormone receptor/binding protein knockout mice
- PMID: 19228785
- PMCID: PMC2667132
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glp017
Reduced incidence and delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic diseases in growth hormone receptor/binding protein knockout mice
Abstract
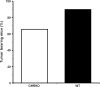
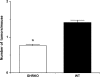
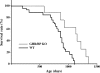
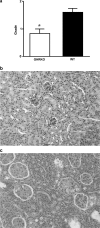
Although studies of Ames and Snell dwarf mice have suggested possible important roles of the growth hormone (GH)/insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) axis in aging and age-related diseases, the results cannot rule out the possibility of other hormonal changes playing an important role in the life extension exhibited by these dwarf mice. Therefore, growth hormone receptor/binding protein (GHR/BP) knockout (KO) mice would be valuable animals to directly assess the roles of somatotropic axis in aging and age-related diseases because the primary hormonal change is due to GH/IGF-1 deficiency. Our pathological findings showed GHR/BP KO mice to have a lower incidence and delayed occurrence of fatal neoplastic lesions compared with their wild-type littermates. These changes of fatal neoplasms are similar to the effects observed with calorie restriction and therefore could possibly be a major contributing factor to the extended life span observed in the GHR/BP KO mice.
Figures

References
-
- Brown-Borg HM, Borg KE, Meliska CJ, Bartke A. Dwarf mice and the ageing process. Nature. 1996;384:33. - PubMed
-
- Miller RA. Kleemeier award lecture: are there genes for aging? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1999;54:B297–B307. - PubMed
-
- Bartke A, Coschigano K, Kopchick J, et al. Genes that prolong life: relationships of growth hormone and growth to aging and life span. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56:B340–B349. - PubMed
-
- Bartke A. Histology of the anterior hypohysis, thyroid and gonads of two types of dwarf mice. Anat Rec. 1964;149:225–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

