Confirming the RNAi-mediated mechanism of action of siRNA-based cancer therapeutics in mice
- PMID: 19229107
- PMCID: PMC2648695
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI37515
Confirming the RNAi-mediated mechanism of action of siRNA-based cancer therapeutics in mice
Abstract
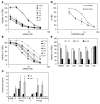
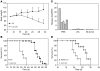
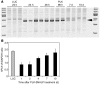
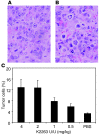
siRNAs that specifically silence the expression of cancer-related genes offer a therapeutic approach in oncology. However, it remains critical to determine the true mechanism of their therapeutic effects. Here, we describe the preclinical development of chemically modified siRNA targeting the essential cell-cycle proteins polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) and kinesin spindle protein (KSP) in mice. siRNA formulated in stable nucleic acid lipid particles (SNALP) displayed potent antitumor efficacy in both hepatic and subcutaneous tumor models. This was correlated with target gene silencing following a single intravenous administration that was sufficient to cause extensive mitotic disruption and tumor cell apoptosis. Our siRNA formulations induced no measurable immune response, minimizing the potential for nonspecific effects. Additionally, RNAi-specific mRNA cleavage products were found in tumor cells, and their presence correlated with the duration of target mRNA silencing. Histological biomarkers confirmed that RNAi-mediated gene silencing effectively inhibited the target's biological activity. This report supports an RNAi-mediated mechanism of action for siRNA antitumor effects, suggesting a new methodology for targeting other key genes in cancer development with siRNA-based therapeutics.
Figures




Comment in
-
Gene silencing below the immune radar.J Clin Invest. 2009 Mar;119(3):438-42. doi: 10.1172/jci38475. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19306498 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

