Altered hematopoiesis in mice lacking DNA polymerase mu is due to inefficient double-strand break repair
- PMID: 19229323
- PMCID: PMC2638008
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000389
Altered hematopoiesis in mice lacking DNA polymerase mu is due to inefficient double-strand break repair
Abstract
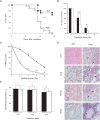
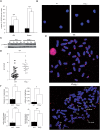
Polymerase micro (Polmicro) is an error-prone, DNA-directed DNA polymerase that participates in non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair. In vivo, Polmicro deficiency results in impaired Vkappa-Jkappa recombination and altered somatic hypermutation and centroblast development. In Polmicro(-/-) mice, hematopoietic development was defective in several peripheral and bone marrow (BM) cell populations, with about a 40% decrease in BM cell number that affected several hematopoietic lineages. Hematopoietic progenitors were reduced both in number and in expansion potential. The observed phenotype correlates with a reduced efficiency in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair in hematopoietic tissue. Whole-body gamma-irradiation revealed that Polmicro also plays a role in DSB repair in non-hematopoietic tissues. Our results show that Polmicro function is required for physiological hematopoietic development with an important role in maintaining early progenitor cell homeostasis and genetic stability in hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Wyman C, Ristic D, Kanaar R. Homologous recombination-mediated double-strand break repair. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:827–833. - PubMed
-
- Lieber MR, Ma Y, Pannicke U, Schwarz K. Mechanism and regulation of human non-homologous DNA end-joining. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:712–720. - PubMed
-
- van Gent DC, Hoeijmakers JH, Kanaar R. Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:196–206. - PubMed
-
- Weterings E, van Gent DC. The mechanism of non-homologous end-joining: a synopsis of synapsis. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:1425–1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

