The empirical valence bond as an effective strategy for computer-aided enzyme design
- PMID: 19229886
- PMCID: PMC2671572
- DOI: 10.1002/biot.200800299
The empirical valence bond as an effective strategy for computer-aided enzyme design
Abstract
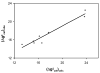
The ability of the empirical valence bond (EVB) to be used in screening active site residues in enzyme design is explored in a preliminary way. This validation is done by comparing the ability of this approach to evaluate the catalytic contributions of various residues in chorismate mutase. It is demonstrated that the EVB model can serve as an accurate tool in the final stages of computer-aided enzyme design (CAED). The ability of the model to predict quantitatively the catalytic power of enzymes should augment the capacity of current approaches for enzyme design.
Figures
Comment in
-
Editorial: Protein design and engineering for biocatalysis.Biotechnol J. 2009 Apr;4(4):439. doi: 10.1002/biot.200900080. Biotechnol J. 2009. PMID: 19370730 No abstract available.
References
-
- Toscano MD, Woycechowsky KJ, Hilvert D. Minimalist active-site redesign: Teaching old enzymes new tricks. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46:4468–4470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources