Biochemical evidence of the interactions of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) with adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT): potential implications linking proteolysis with energy metabolism in cancer cells
- PMID: 19232058
- PMCID: PMC2737480
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20090082
Biochemical evidence of the interactions of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) with adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT): potential implications linking proteolysis with energy metabolism in cancer cells
Abstract
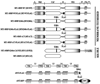
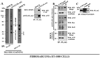
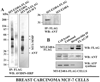
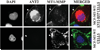
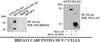
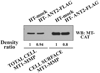
Invasion-promoting MT1-MMP (membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase) is a key element in cell migration processes. To identify the proteins that interact and therefore co-precipitate with this proteinase from cancer cells, we used the proteolytically active WT (wild-type), the catalytically inert E240A and the C-end truncated (tailless; DeltaCT) MT1-MMP-FLAG constructs as baits. The identity of the pulled-down proteins was determined by LC-MS/MS (liquid chromatography tandem MS) and then confirmed by Western blotting using specific antibodies. We determined that, in breast carcinoma MCF cells (MCF-7 cells), ANT (adenine nucleotide translocator) efficiently interacted with the WT, E240A and DeltaCT constructs. The WT and E240A constructs also interacted with alpha-tubulin, an essential component of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. In turn, tubulin did not co-precipitate with the DeltaCT construct because of the inefficient endocytosis of the latter, thus suggesting a high level of selectivity of our test system. To corroborate these results, we then successfully used the ANT2-FLAG construct as a bait to pull-down MT1-MMP, which was naturally produced by fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. We determined that the presence of the functionally inert catalytic domain alone was sufficient to cause the proteinase to interact with ANT2, thus indicating that there is a non-proteolytic mode of these interactions. Overall, it is tempting to hypothesize that by interacting with pro-invasive MT1-MMP, ANT plays a yet to be identified role in a coupling mechanism between energy metabolism and pericellular proteolysis in migrating cancer cells.
Figures

References
-
- Wolf K, Wu YI, Liu Y, Geiger J, Tam E, Overall C, Stack MS, Friedl P. Multi-step pericellular proteolysis controls the transition from individual to collective cancer cell invasion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007;9:893–904. - PubMed
-
- Strongin AY. Mislocalization and unconventional functions of cellular MMPs in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:87–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

